How to Learn Embedded Systems: A Step-by-Step Guide for Manufacturers
Discover essential steps on how to learn embedded systems for effective manufacturing...

Understanding the complexities of Machine-to-Machine (M2M) technology is crucial for medical device manufacturers who seek to improve patient care and operational efficiency. This guide explores the essential elements of M2M, illustrating how it enables seamless data exchange between devices and ultimately transforms healthcare delivery. As the adoption of M2M technology accelerates, manufacturers must navigate various challenges to fully harness its potential in enhancing medical outcomes.
To define m2m, it is important to note that Machine-to-Machine (M2M) technology facilitates the automated transfer of information between devices without human intervention, utilizing various communication channels, including wired and wireless networks. To define m2m, one must understand that it is a fundamental component of the Internet of Things (IoT) that empowers devices to autonomously share information and perform tasks, significantly enhancing operational efficiency within healthcare settings. To define M2M, one must consider key components such as sensors, communication modules, and processing units, which collectively enable medical devices - such as wearable gadgets, heart pumps, and liquid biopsy platforms - to improve functionality and patient care.
To define m2m, it refers to M2M technology that enables devices to transmit and receive data seamlessly, facilitating real-time monitoring and control of medical conditions. For instance, wearable health monitors can help define m2m by sending vital statistics directly to medical providers, thereby enhancing remote management of patients.
To define M2M, it is important to note that M2M devices are capable of connecting through various networks, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, ensuring robust communication capabilities across diverse environments.
To define M2M, the primary advantage of this technology lies in its capacity to automate processes, thereby minimizing the need for human oversight. This automation not only streamlines operations but also mitigates the risk of human error, ultimately improving patient safety.
Real-world applications that help define M2M information exchange in healthcare underscore its transformative potential. Continuous glucose monitors, for example, utilize M2M technology to define m2m and transmit real-time data to monitoring services, facilitating improved diabetes management. Recent trends indicate a notable increase in the adoption of home monitoring services with integrated connectivity, reflecting the growing trend of remote health monitoring. To define m2m, the integration of M2M technologies is expected to enhance user engagement and self-care, leading to improved health outcomes and operational efficiencies within the medical device sector.
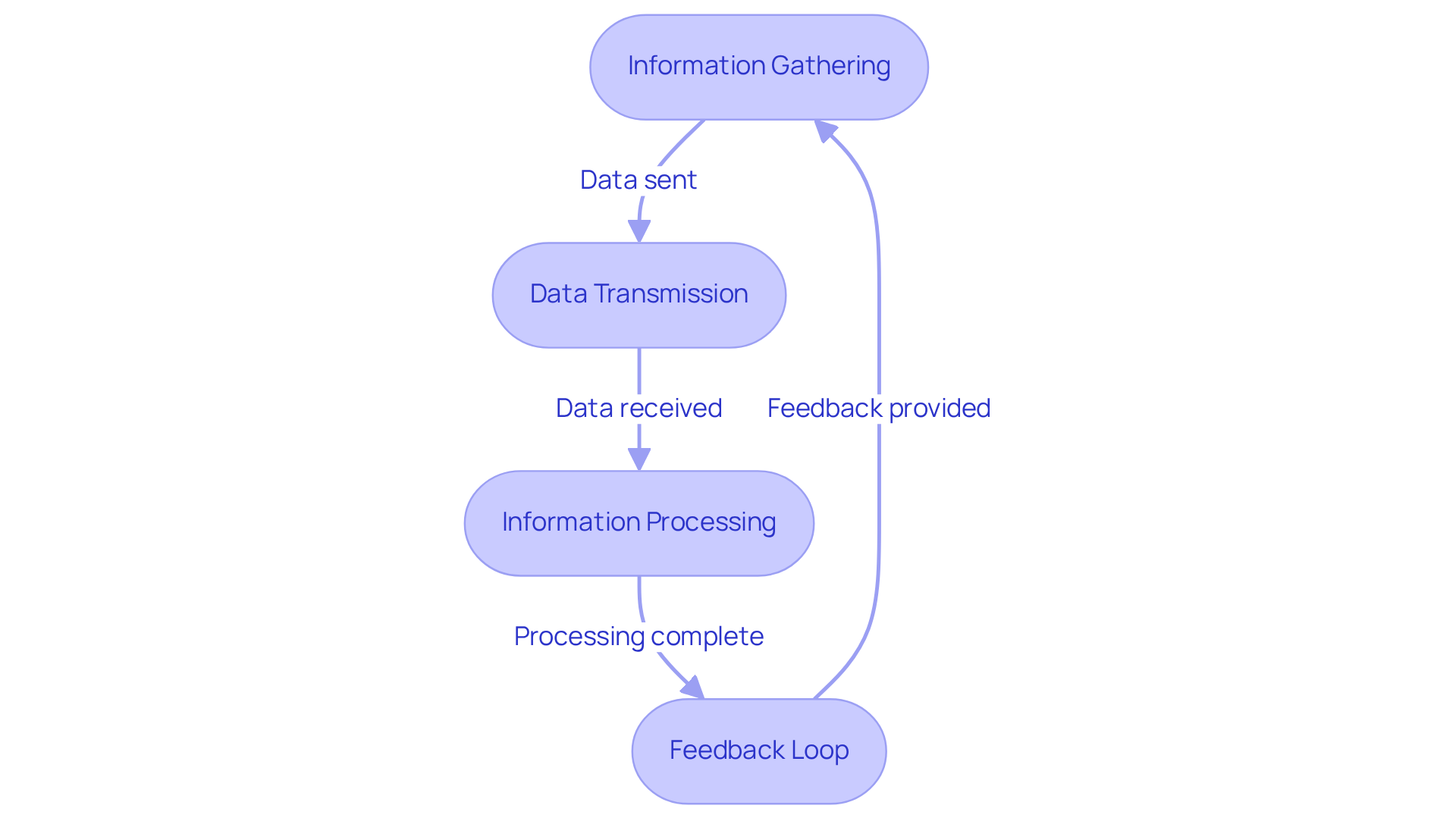
M2M communication in healthcare encompasses a systematic process of data collection, transmission, and processing, which can be outlined as follows:
In a remote patient monitoring setup, a wearable device continuously collects heart rate data and transmits it to a healthcare provider's server. If the heart rate exceeds a predetermined limit, the system promptly notifies the medical provider, enabling swift intervention. This automated data exchange not only enhances individual monitoring but also significantly reduces the potential for human error, which helps to define M2M communication as a crucial component in modern medical services.
According to Laura Gaber, 'Telemedicine applications have been driven primarily by situations in which the doctor or specialist and individual are physically separated,' which emphasizes the importance to define M2M communication in facilitating remote care. Furthermore, healthcare providers monitored approximately 308,000 individuals globally for various conditions last year, which helps to define M2M technologies and their growing reliance in healthcare. With access to over 400 networks in more than 200 countries, M2M SIM cards ensure uninterrupted information flow, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of telehealth solutions.
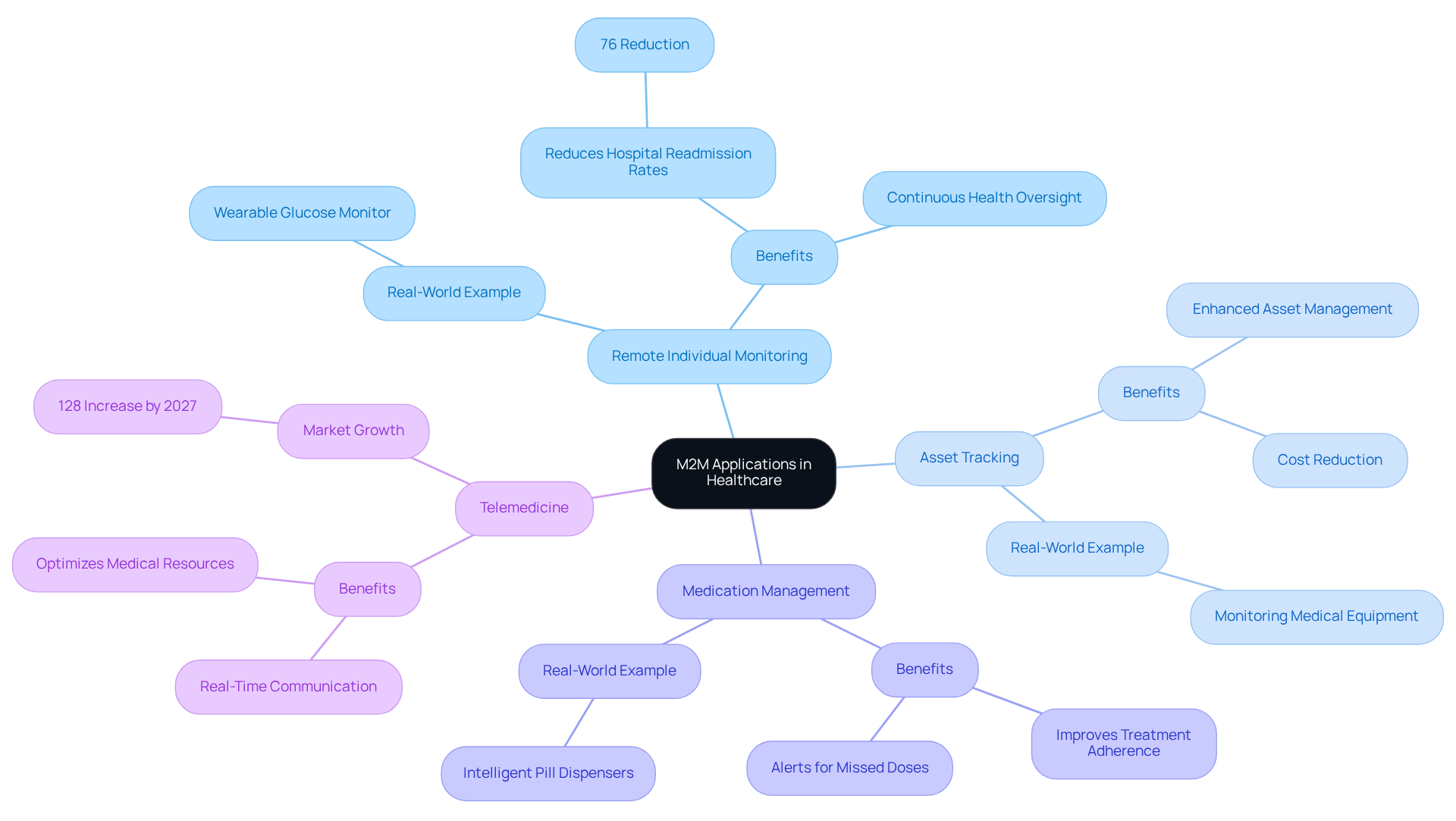
To define M2M, it is important to recognize that this technology plays a crucial role in the medical field, significantly enhancing care and operational efficiency. Below are key applications:
Remote Individual Monitoring: Devices that continuously track vital signs can transmit information to medical providers, facilitating ongoing oversight of individuals without necessitating in-person visits. This approach has been shown to reduce hospital readmission rates by as much as 76%, underscoring its effectiveness in managing individual health. Recent advancements in cardiac monitoring illustrate the shift from tethered systems to truly wireless solutions, exemplifying Voler Systems' commitment to innovation.
Asset Tracking: Hospitals utilize M2M technology to monitor the location and usage of costly medical equipment. This capability enhances asset management, reduces expenses, and ensures that critical devices are available when needed.
Medication Management: Intelligent pill dispensers equipped with M2M technology can alert users when it is time to take their medication and notify medical professionals if doses are missed. This proactive strategy improves adherence to treatment plans and enhances outcomes for individuals.
Telemedicine: M2M facilitates real-time communication between individuals and medical practitioners, enabling remote consultations and follow-ups. This technology not only enhances convenience for individuals but also optimizes medical resources, as evidenced by the anticipated growth of remote monitoring systems, projected to increase by 128% by 2027.
Real-World Example: A wearable glucose monitor exemplifies M2M technology in action, transmitting blood sugar levels to both a patient's smartphone and their healthcare provider. This immediate information exchange allows for timely adjustments to insulin dosage, which helps to define M2M's potential to improve chronic disease management. Furthermore, innovative devices, such as a calf-worn device designed for motion and circumference monitoring, demonstrate how M2M applications are evolving to support rehabilitation and compliance with medical device standards.
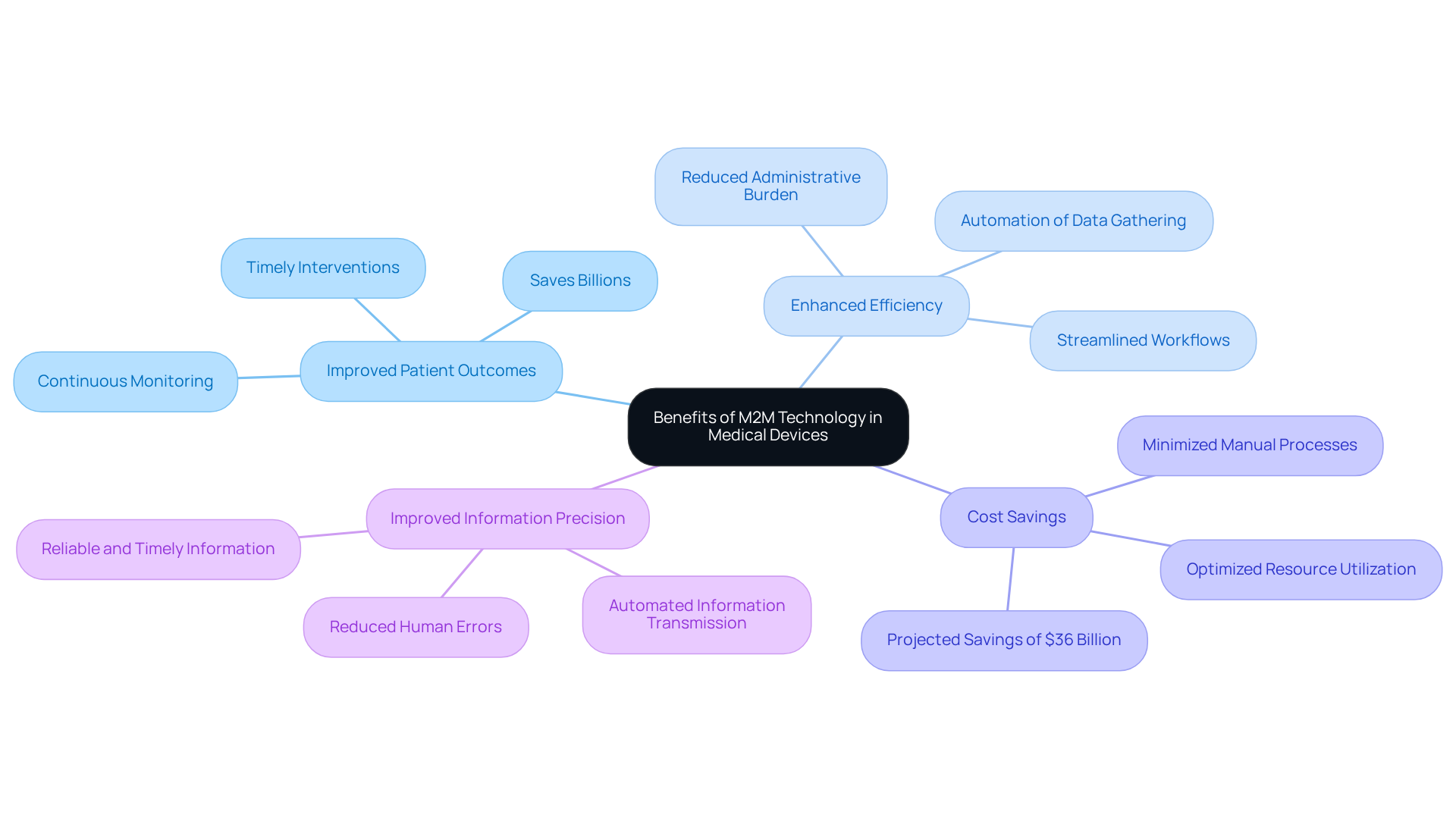
Implementing M2M technology in medical devices offers substantial advantages, including:
Summary of Benefits:
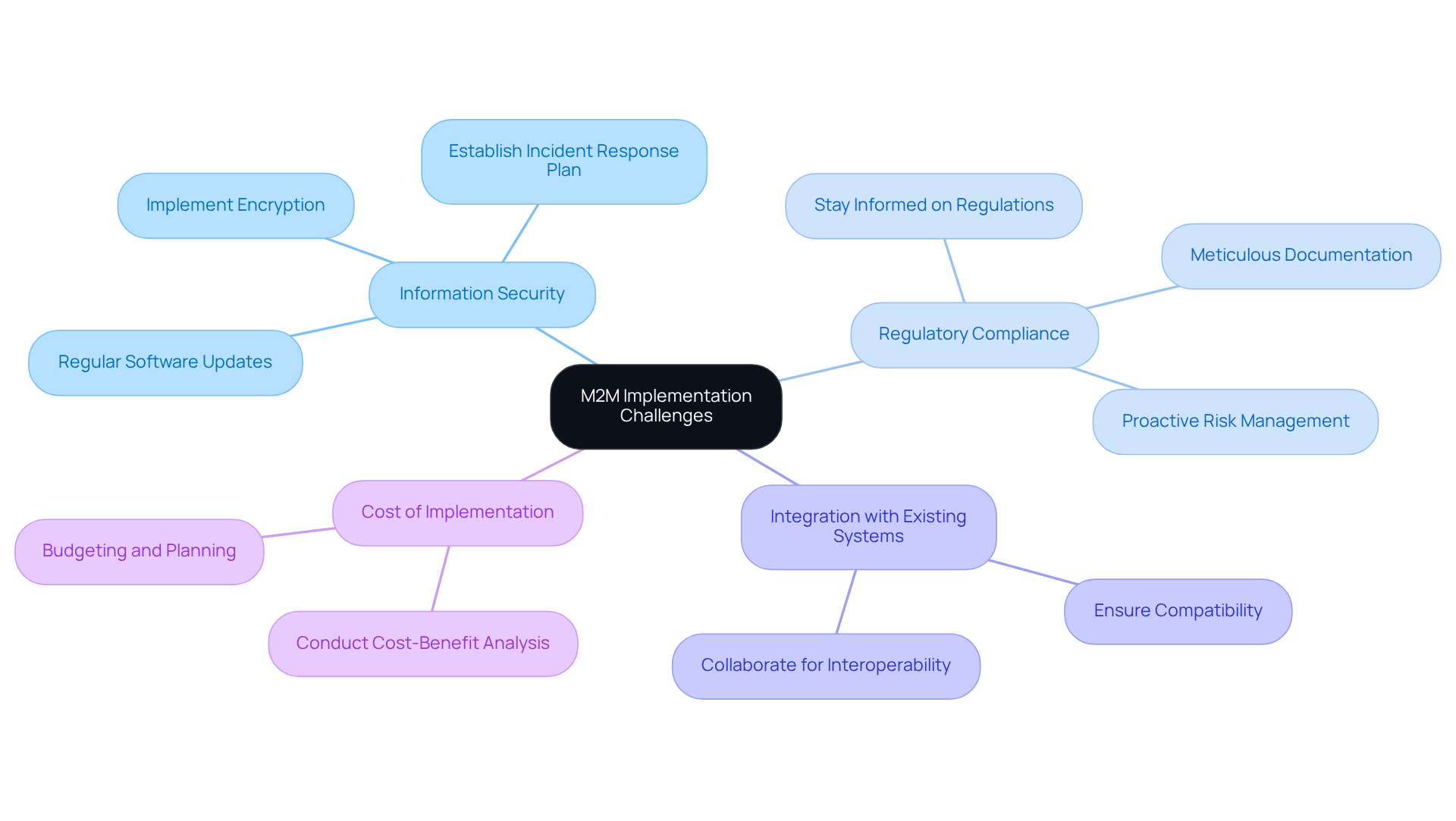
M2M technology offers significant advantages for medical device manufacturers, but it also presents several challenges that require careful consideration:
Information Security: Protecting transmitted information is crucial, as breaches can jeopardize patient privacy and safety. To define M2M, one must consider how the interconnected nature of M2M systems heightens the risk of unauthorized access, making robust cybersecurity measures imperative.
Regulatory Compliance: Medical devices must adhere to stringent regulatory standards, complicating the integration of M2M technology. Compliance with frameworks such as the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (QSR) and the forthcoming Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) necessitates meticulous documentation and proactive risk management.
To define M2M, it is essential that these systems integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare infrastructures, which can vary significantly across organizations. Ensuring compatibility is vital for effective communication and information exchange.
Cost of Implementation: The initial investment required for M2M technology can be considerable, necessitating careful budgeting and planning to secure a favorable return on investment.
M2M technology represents a significant force in the medical device sector, facilitating seamless communication between devices and enhancing patient care through automation and real-time data exchange. By grasping the fundamentals of M2M, manufacturers can leverage this technology to markedly improve operational efficiency and patient outcomes.
This article highlights essential components of M2M, including its communication processes, various applications such as remote monitoring and medication management, and the numerous benefits it offers, including enhanced patient outcomes and cost savings. Furthermore, it addresses the challenges of implementation, such as information security and regulatory compliance, while providing strategies to overcome these barriers.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, embracing M2M technology is not merely an option but a necessity for medical device manufacturers aiming to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. Thus, investing in M2M solutions will not only improve health outcomes but also position organizations at the forefront of innovation in the medical field. The future of healthcare relies on the integration of these technologies, making it imperative to prioritize M2M in strategic planning and development.
What is M2M technology?
M2M (Machine-to-Machine) technology facilitates the automated transfer of information between devices without human intervention, utilizing various communication channels, including wired and wireless networks.
How does M2M technology relate to the Internet of Things (IoT)?
M2M technology is a fundamental component of the IoT that empowers devices to autonomously share information and perform tasks, significantly enhancing operational efficiency, particularly in healthcare settings.
What are the key components of M2M technology?
Key components include sensors, communication modules, and processing units, which enable medical devices like wearable gadgets and heart pumps to improve functionality and patient care.
How does M2M technology enhance patient care?
M2M technology allows devices to transmit and receive data seamlessly, facilitating real-time monitoring and control of medical conditions, such as wearable health monitors sending vital statistics directly to medical providers.
What types of networks do M2M devices connect through?
M2M devices can connect through various networks, including cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, ensuring robust communication capabilities across diverse environments.
What is the primary advantage of M2M technology?
The primary advantage of M2M technology is its capacity to automate processes, minimizing the need for human oversight, streamlining operations, and reducing the risk of human error, ultimately improving patient safety.
Can you provide an example of M2M technology in healthcare?
Continuous glucose monitors utilize M2M technology to transmit real-time data to monitoring services, facilitating improved diabetes management.
What recent trends are observed in M2M technology adoption?
There is a notable increase in the adoption of home monitoring services with integrated connectivity, reflecting the growing trend of remote health monitoring.
How does M2M communication work in healthcare?
M2M communication in healthcare involves a systematic process of information gathering by medical devices, data transmission through communication modules, information processing, and a feedback loop for real-time adjustments.
What is an example scenario of M2M communication in action?
In a remote patient monitoring setup, a wearable device collects heart rate data and transmits it to a healthcare provider's server. If the heart rate exceeds a predetermined limit, the system notifies the medical provider for swift intervention.
How many individuals were monitored globally using M2M technologies last year?
Healthcare providers monitored approximately 308,000 individuals globally for various conditions last year, highlighting the growing reliance on M2M technologies in healthcare.
What role do M2M SIM cards play in healthcare?
M2M SIM cards provide access to over 400 networks in more than 200 countries, ensuring uninterrupted information flow and enhancing the effectiveness of telehealth solutions.
