Define M2M: A Step-by-Step Guide for Medical Device Manufacturers
Learn how to define M2M technology and its impact on medical device manufacturing.

Design for Manufacturing (DFM) represents a critical strategy within the medical device industry, where precision is essential and the stakes are notably high. By incorporating manufacturing considerations at the outset of the design process, manufacturers can streamline production, improve product quality, and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Nevertheless, the path to successful DFM implementation is not without its challenges, ranging from intricate assembly procedures to the ever-evolving landscape of regulatory requirements.
How can manufacturers effectively navigate these obstacles to fully realize the potential of DFM, ensuring that their products not only meet market demands but also adhere to safety regulations?
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a strategic engineering approach that streamlines the manufacturing process by embedding manufacturing considerations into the product design phase. This methodology is crucial in the medical device industry, where compliance with stringent regulatory standards and maintaining high-quality benchmarks are paramount. By adopting DFM principles, manufacturers can foresee potential production challenges, leading to designs that are simpler to produce, assemble, and test. This proactive approach not only accelerates time-to-market but also significantly reduces costs.
As of 2026, trends in DFM emphasize modular manufacturing and circular practices, which focus on reusing materials and minimizing environmental impact. These innovations align with the industry's shift towards sustainability and efficiency, as highlighted by recent advancements in circular manufacturing and 3D printing technologies. Statistics reveal that companies implementing DFM strategies experience a notable decrease in non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs, enhancing their competitive edge. For instance, automated test systems and off-the-shelf hardware have been shown to reduce NRE costs significantly, according to industry reports.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced technologies, such as 5G connectivity, facilitates real-time data exchange, improving diagnostics and remote monitoring capabilities. Successful DFM implementation is exemplified by companies that leverage off-the-shelf testing hardware and automated systems, which not only expedite production timelines but also ensure compliance with evolving regulatory demands. As Matthew Thompson, Engineering & Sales Manager - Strategic Initiatives, states, "To build future-ready medical device manufacturing, companies are outsourcing test and quality processes to leverage best practice experiences." Staying informed about the latest DFM developments is essential for manufacturers aiming to thrive in the fast-paced medical device landscape.
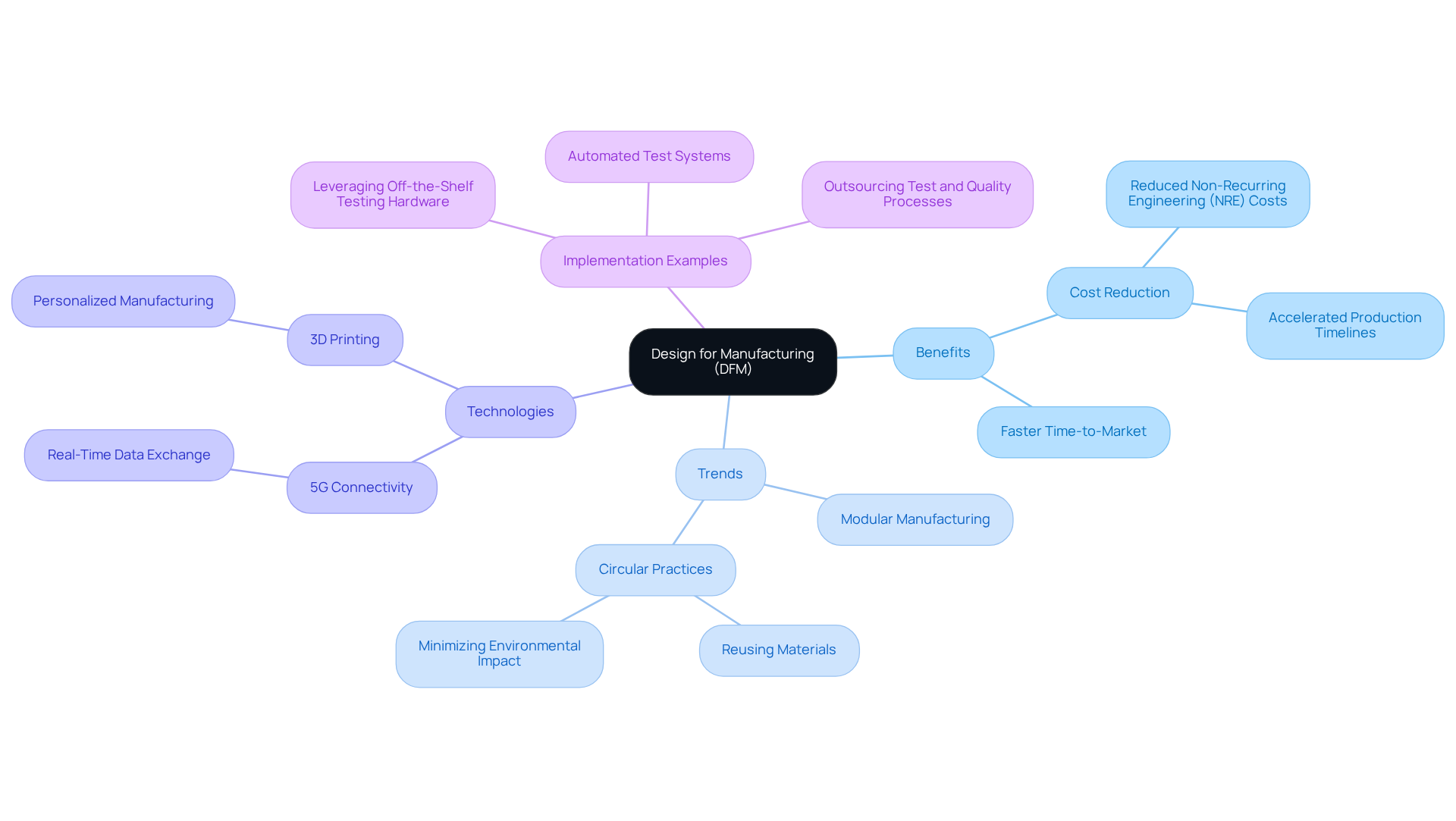
Key principles of Design for Manufacturability (DFM) in medical devices include:
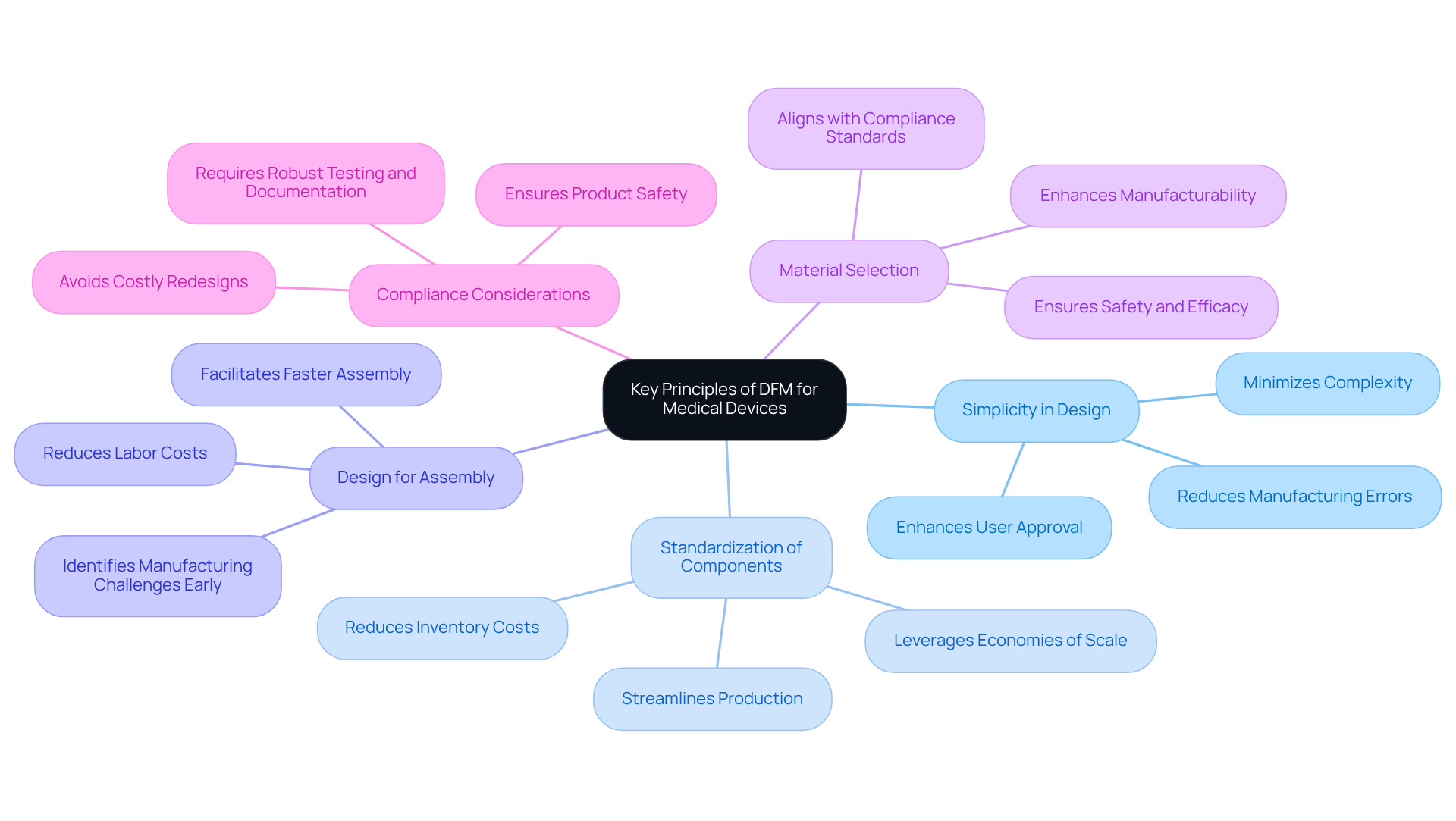
Simplicity in Design: Striving for simplicity minimizes complexity, significantly reducing manufacturing errors and associated costs. Streamlined layouts often lead to more effective manufacturing methods and can enhance user approval. Voler Systems emphasizes that simplifying the layout, without compromising functionality, can yield substantial cost reductions while maintaining the device’s effectiveness.
Standardization of Components: Utilizing common parts across various products streamlines production and reduces inventory costs. This approach simplifies assembly and leverages economies of scale, lowering per-unit costs as production volume increases. By standardizing components, Voler Systems aids clients in enhancing their production methods.
Design for Assembly: Ensuring that components are easy to assemble can drastically reduce labor costs and assembly time. Modular structures facilitate this process, enabling faster assembly with minimal specialized tools. Early collaboration with manufacturers, such as Voler Systems, helps identify potential manufacturing challenges and ensures feasibility, particularly during prototype development.
Material Selection: Choosing readily available and easy-to-work-with materials enhances manufacturability and can lead to cost savings. Biocompatible and regulatory-compliant materials are essential for medical devices, ensuring safety and efficacy. Voler Systems prioritizes material selection that aligns with compliance standards, facilitating smoother transitions from prototype to production.
Compliance Considerations: Designing with regulatory requirements in mind helps avoid costly redesigns and ensures that products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. Robust testing and thorough documentation are critical for compliance with these regulations. By addressing manufacturability challenges early, Voler Systems helps to define DFM, enabling innovative concepts to be produced reliably while focusing on compliance throughout the development phase.
By adhering to these principles, manufacturers can develop medical devices that are not only innovative but also practical, cost-effective, and compliant with industry standards.
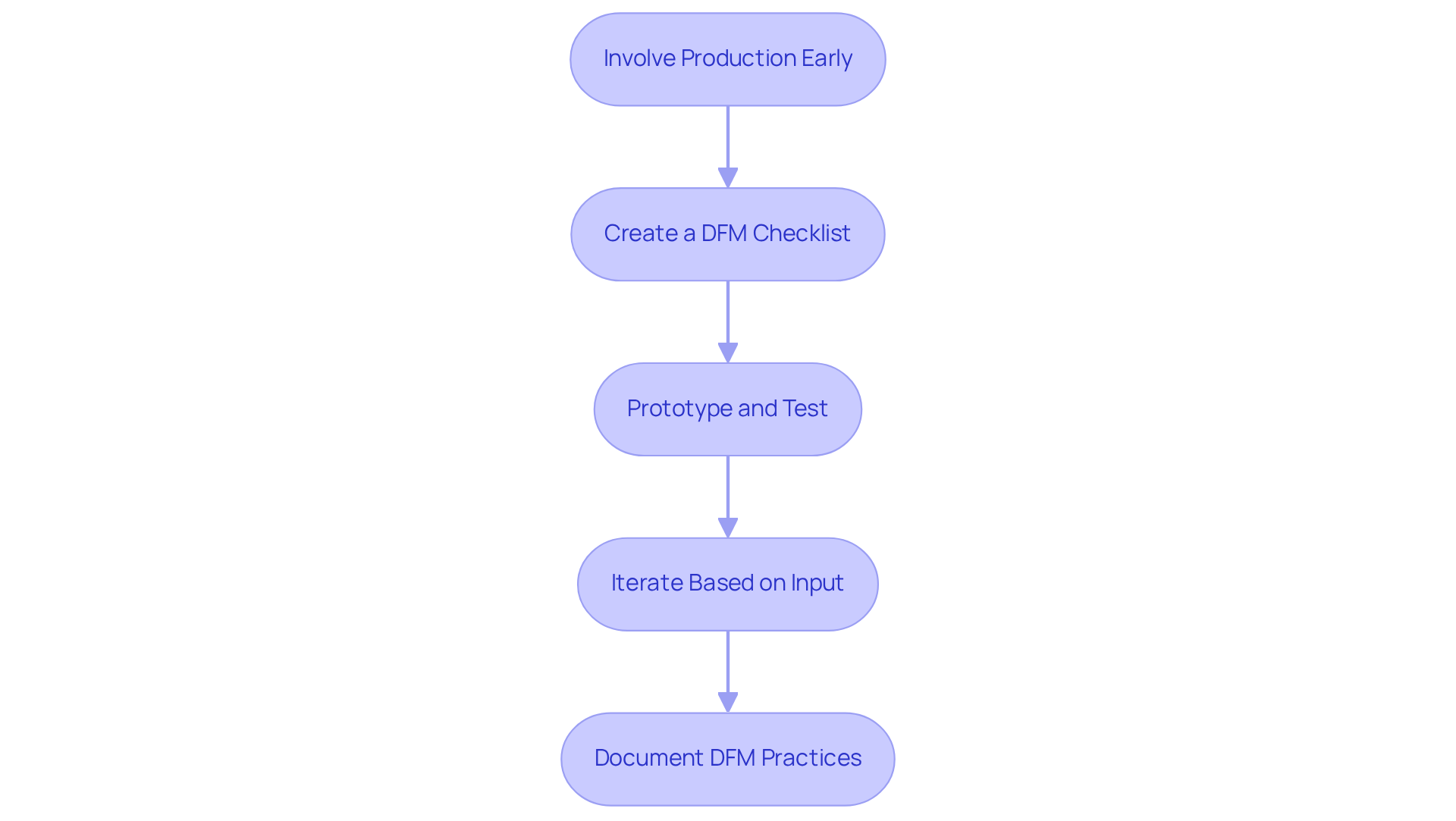
To effectively implement DFM strategies in your design process, consider the following steps:
Involve Production Early: Engage production specialists from the outset to identify potential challenges and opportunities for improvement. Early engagement can significantly reduce production-related issues later in development, as evidenced by successful projects that integrated production insights during the planning phase. Common errors, such as overlooking material constraints or assembly difficulties, can be mitigated through this proactive approach.
Create a DFM Checklist: Develop a comprehensive checklist that encompasses key DFM principles. This tool will help to define dfm by guiding your design choices and ensuring alignment with production capabilities, ultimately enhancing product quality and reducing costs. Including common pitfalls in this checklist can further assist in avoiding mistakes during production tests.
Prototype and Test: Create prototypes early in the development process to identify any manufacturability issues. Statistics indicate that early prototyping can lead to a 30% reduction in production costs by allowing modifications before large-scale production begins. Furthermore, incorporating adequate and accessible test points in layouts simplifies in-circuit testing and functional testing, thereby improving quality control without increasing time or expense. Common errors, such as inadequate test point placement, can be identified and corrected at this stage.
Iterate Based on Input: Utilize insights from production teams to refine concepts. This iterative process should focus on simplifying assembly and minimizing costs, as demonstrated in case studies where early adjustments resulted in improved product performance and reduced field failures. Common errors, like complex assembly sequences, can be addressed through this feedback loop. As Pletcher notes, "A product will get out the door better and faster if all are gathered around the drawing board."
Document DFM Practices: Maintain thorough documentation of DFM practices and decisions. This record not only ensures consistency across projects but also serves as a valuable reference for future developments, facilitating compliance with stringent regulatory requirements. It is essential to operate in a development environment that provides complete traceability to any production and simulation data, ensuring that decisions are thoroughly recorded for regulatory purposes. Documenting common errors encountered during testing can also provide insights for future projects.
By following these steps, manufacturers can define dfm to develop concepts that are not only innovative but also optimized for efficient production, ultimately leading to improved market readiness and enhanced product reliability.
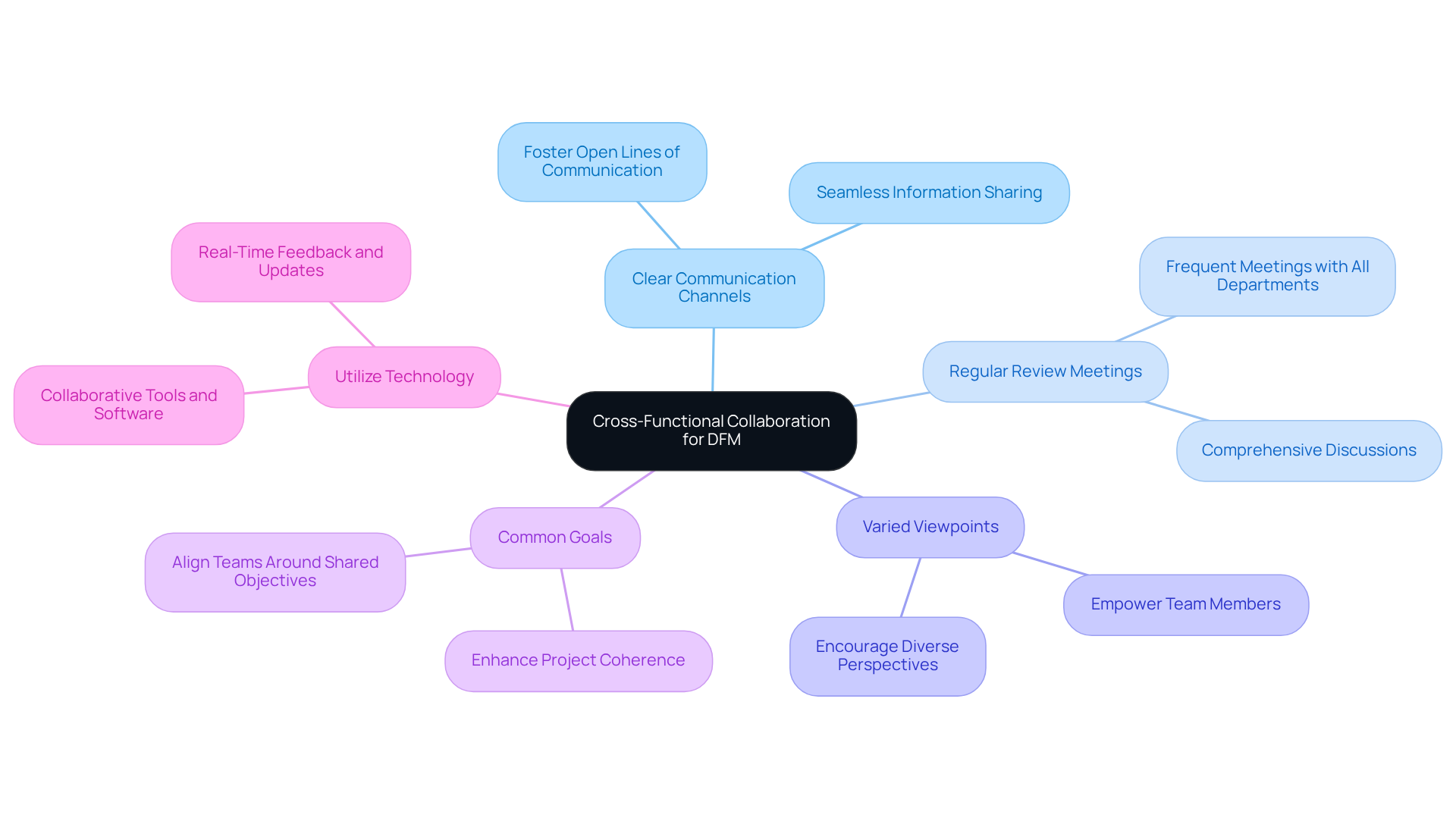
To enhance cross-functional collaboration for effective Design for Manufacturability (DFM), organizations should implement the following strategies:
Establish Clear Communication Channels: Foster open lines of communication among creative, engineering, manufacturing, and quality assurance teams. This facilitates seamless information sharing and ensures that all parties are informed and engaged.
Conduct Regular Review Meetings: Schedule frequent review meetings that include representatives from all relevant departments. This allows for comprehensive discussions on decisions and the gathering of diverse input, which is crucial for informed decision-making.
Promote Varied Viewpoints: Create an atmosphere where team members feel empowered to express their thoughts and recommendations. Encouraging diverse perspectives can lead to innovative solutions and improved outcomes.
Set Common Goals: Align all teams around shared objectives related to manufacturability, quality, and compliance. This alignment ensures that everyone is working towards the same outcomes, enhancing overall project coherence.
Utilize Technology: Employ collaborative tools and software that facilitate real-time feedback and updates. This optimizes the creative workflow and improves teamwork, making the process more efficient.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to define DFM, leading to higher quality and more efficient medical device development methods.
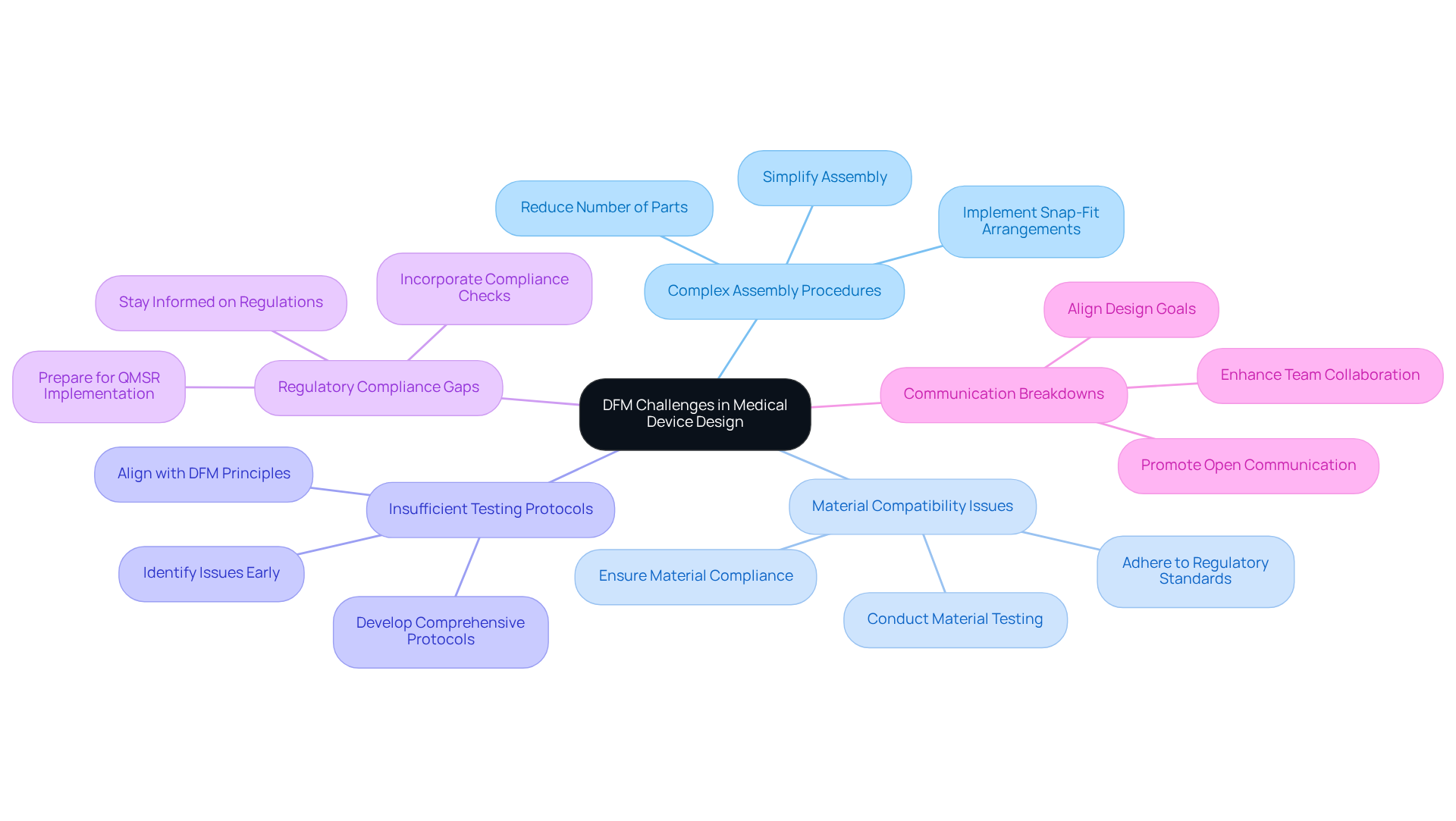
Common DFM challenges in medical device design include:
Complex Assembly Procedures: When assembly becomes overly intricate, it is advisable to rework components to simplify the task. This can involve reducing the number of parts or implementing snap-fit arrangements to facilitate easier assembly.
Material Compatibility Issues: It is essential to ensure that the selected materials are compatible with manufacturing methods and adhere to regulatory standards. Conducting thorough material testing is crucial to prevent complications during production.
Insufficient Testing Protocols: Developing comprehensive testing protocols that align with DFM principles is vital for identifying potential issues early in the development phase. This proactive approach can save time and resources.
Regulatory Compliance Gaps: Staying informed about regulatory requirements is critical, particularly with the impending implementation of the Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) in 2026. Incorporating compliance checks throughout the development process can help avoid costly redesigns later. Voler Systems provides expertise in documentation compliance support, assisting manufacturers in navigating these regulatory challenges effectively.
Communication Breakdowns: Promoting a culture of open communication among teams is essential to ensure alignment on design goals and challenges. This collaborative approach can enhance problem-solving and innovation.
By proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can define DFM to improve their practices and increase the overall success of their medical device projects. Industry experts emphasize that maintaining compliance and adapting to evolving regulatory expectations are crucial for achieving long-term success in the medical device sector. Voler Systems plays a vital role in supporting the development of innovative medical technology.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a crucial framework for medical device manufacturers, highlighting the necessity of integrating manufacturing considerations into the design process. By implementing DFM principles, organizations can optimize production, improve product quality, and adhere to stringent regulatory standards. This proactive strategy not only shortens time-to-market but also significantly lowers costs, making it indispensable for manufacturers striving to succeed in a competitive environment.
The article discusses key DFM principles, including:
It emphasizes the significance of early collaboration with production teams and the establishment of comprehensive testing protocols as essential strategies for successful DFM implementation. Furthermore, fostering cross-functional collaboration and ensuring clear communication channels are identified as critical for addressing common challenges in the medical device development process.
Ultimately, adopting DFM transcends mere manufacturing efficiency; it promotes innovation and guarantees that medical devices adhere to the highest safety and efficacy standards. Manufacturers are urged to actively apply DFM strategies and stay updated on the latest trends and technologies. By doing so, they can enhance their product offerings, reduce costs, and contribute to the advancement of healthcare solutions, thereby making a lasting impact on the industry.
What is Design for Manufacturing (DFM)?
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a strategic engineering approach that integrates manufacturing considerations into the product design phase, aimed at streamlining the manufacturing process, particularly in the medical device industry.
Why is DFM important in the medical device industry?
DFM is crucial in the medical device industry due to the need for compliance with stringent regulatory standards and maintaining high-quality benchmarks, which helps in foreseeing potential production challenges and simplifying the manufacturing process.
What are the benefits of adopting DFM principles?
Adopting DFM principles can accelerate time-to-market, significantly reduce costs, and lead to designs that are easier to produce, assemble, and test.
What trends in DFM are emerging as of 2026?
Trends include modular manufacturing and circular practices that focus on reusing materials and minimizing environmental impact, aligning with the industry's shift towards sustainability and efficiency.
How does DFM impact non-recurring engineering (NRE) costs?
Companies implementing DFM strategies often experience a notable decrease in NRE costs, which enhances their competitive edge, as evidenced by the use of automated test systems and off-the-shelf hardware.
What role does technology play in DFM?
Advanced technologies, such as 5G connectivity, enable real-time data exchange, improving diagnostics and remote monitoring capabilities, which are essential for successful DFM implementation.
What are the key principles of DFM for medical devices?
Key principles include: - Simplicity in Design: Minimizing complexity to reduce manufacturing errors and costs. - Standardization of Components: Using common parts to streamline production and lower inventory costs. - Design for Assembly: Ensuring components are easy to assemble to reduce labor costs and assembly time. - Material Selection: Choosing readily available and compliant materials to enhance manufacturability. - Compliance Considerations: Designing with regulatory requirements in mind to avoid costly redesigns and ensure safety.
How can manufacturers ensure compliance while implementing DFM?
Manufacturers can ensure compliance by addressing manufacturability challenges early, conducting robust testing, and maintaining thorough documentation to meet regulatory standards.
