Why IoT Microcontrollers Are Essential for Medical Device Innovation
Discover the critical role of IoT microcontrollers in advancing medical device innovation.

Embedded operating systems serve as the foundation for devices that define modern technology, encompassing everything from medical equipment to smart home devices. These specialized systems are designed for efficiency and real-time performance, rendering them essential in an age where precision and reliability are critical. As industries evolve and adopt advanced technologies, however, challenges emerge in comprehending and effectively implementing these systems. An exploration of the significance and characteristics of embedded operating systems not only highlights their vital role in current applications but also underscores the future implications for innovation across various sectors.
An integrated software platform is a specialized application designed to manage hardware and software resources in integrated devices. In contrast to general-purpose platforms that cater to a wide range of tasks, what is an embedded OS refers to a specialized operating system tailored for dedicated applications, often operating under real-time constraints. By 2026, it is projected that approximately 70% of healthcare equipment will utilize integrated software platforms, highlighting their critical role in ensuring efficiency and compliance with industry regulations. These frameworks are vital for devices that perform specific functions, such as medical instruments, automotive technologies, and consumer electronics.
Key characteristics of integrated software solutions include:
These characteristics ensure that equipment operates effectively within their designated environments. For instance, in healthcare technology, integrated operating system platforms facilitate the seamless operation of devices like wearable sensors and heart pumps, which require precise control and immediate data processing. As industries increasingly adopt advanced technologies, learning what is an embedded OS is expected to become crucial, making it indispensable for the future of medical equipment and beyond.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, it's essential to understand what is an embedded OS, as these operating platforms are becoming increasingly vital in the evolving landscape of medical technology. These specialized systems are designed to perform specific tasks with high efficiency and real-time responsiveness, which is crucial for applications such as medical monitoring instruments. The dependability of these tools relies on the features of integrated operating systems, illustrating what is an embedded OS, which enhance functionality while adhering to rigorous performance and safety standards.
In 2026, the integration of operating systems in medical monitoring technology is expected to significantly improve equipment reliability and patient outcomes. For instance, advanced integrated technologies facilitate continuous monitoring of vital signs, enabling prompt interventions and reducing the risk of complications. The adoption of lightweight and highly configurable real-time operating systems (RTOS), which are a type of what is an embedded OS, is particularly noteworthy, as they are engineered to optimize power consumption and bolster security features, essential for battery-operated medical devices.
Real-world examples illustrate what is an embedded OS and how it has a transformative impact on medical monitoring equipment. For example, wearable health monitors equipped with sophisticated integrated operating systems can analyze data in real-time, providing healthcare professionals with immediate insights into patient conditions. This capability not only enhances the accuracy of monitoring but also supports proactive healthcare management, aligning with the latest advancements in cardiac monitoring, as demonstrated in the case study of a confidential medical technology innovator.
As the demand for connected medical equipment rises, the role of integrated operating systems will become increasingly significant, driving innovation and ensuring that tools meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients alike. The ongoing advancements in integrated OS technology, including trends such as AI and machine learning at the edge, will continue to shape the future of medical monitoring, establishing these frameworks as a fundamental component of contemporary electronic design in the healthcare sector.
What is an embedded OS is defined by efficiency, reliability, and real-time performance, which are essential for a wide range of applications, particularly in the medical device sector where innovations like Edge AI are becoming increasingly significant. Key characteristics include:
Real-Time Operation: Many embedded systems require immediate processing and response to external events, making real-time capabilities essential. In fact, approximately 70% of embedded developers are projected to utilize Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) by 2025, underscoring the demand for deterministic behavior in complex applications. Industry observers note that "Embedded RTOS platforms represent a foundational element for IoT advancements, emphasizing secure, portable, and certifiable solutions."
Resource Limitations: Embedded software is crafted to function within limited hardware resources, optimizing memory and processing capabilities to ensure efficient performance in constrained environments. This is particularly relevant as the trend toward low-power design in wearable technology continues to grow, driven by the demand for extended battery life and efficiency in medical applications.
Task-Specific Functionality: Unlike general-purpose platforms, specialized operating systems are tailored for specific applications, ensuring optimized performance that meets the distinct needs of various sectors, including the evolving landscape of medical tools that leverage AI for enhanced functionality.
The primary types of embedded operating systems include:
Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS): These systems are designed for applications requiring precise timing and reliability, making them ideal for sectors such as automotive and medical devices. For example, embOS is recognized for its medical-grade safety and stability, specifically catering to low-power medical and industrial microcontrollers. Its certifications ensure compliance with stringent safety standards, making it a preferred choice in critical applications.
Integrated Linux: This platform is widely adopted in numerous integrated applications due to its adaptability and robust community support, rendering it suitable for various use cases, including wearable technology that increasingly incorporates AI features.
Bare-Metal Environments: Operating without an OS, these setups provide maximum efficiency for simple tasks, often employed in applications where resource optimization is crucial.
Understanding these traits and categories is vital for developers when selecting the appropriate platform for their integrated applications, particularly as knowing what is an embedded OS will be essential in a market for integrated platforms that is anticipated to grow significantly, reaching USD 15.2 billion by 2033. This growth reflects the evolving demands of the medical and IoT sectors, where responsiveness and efficiency are paramount. Additionally, challenges such as security vulnerabilities and integration complexities must be considered, as they pose substantial barriers to the adoption of embedded software. As the landscape evolves, the integration of AI and edge computing will further influence platform selection, particularly in IoT applications, highlighting the innovative direction that Voler Systems is pursuing in this domain.
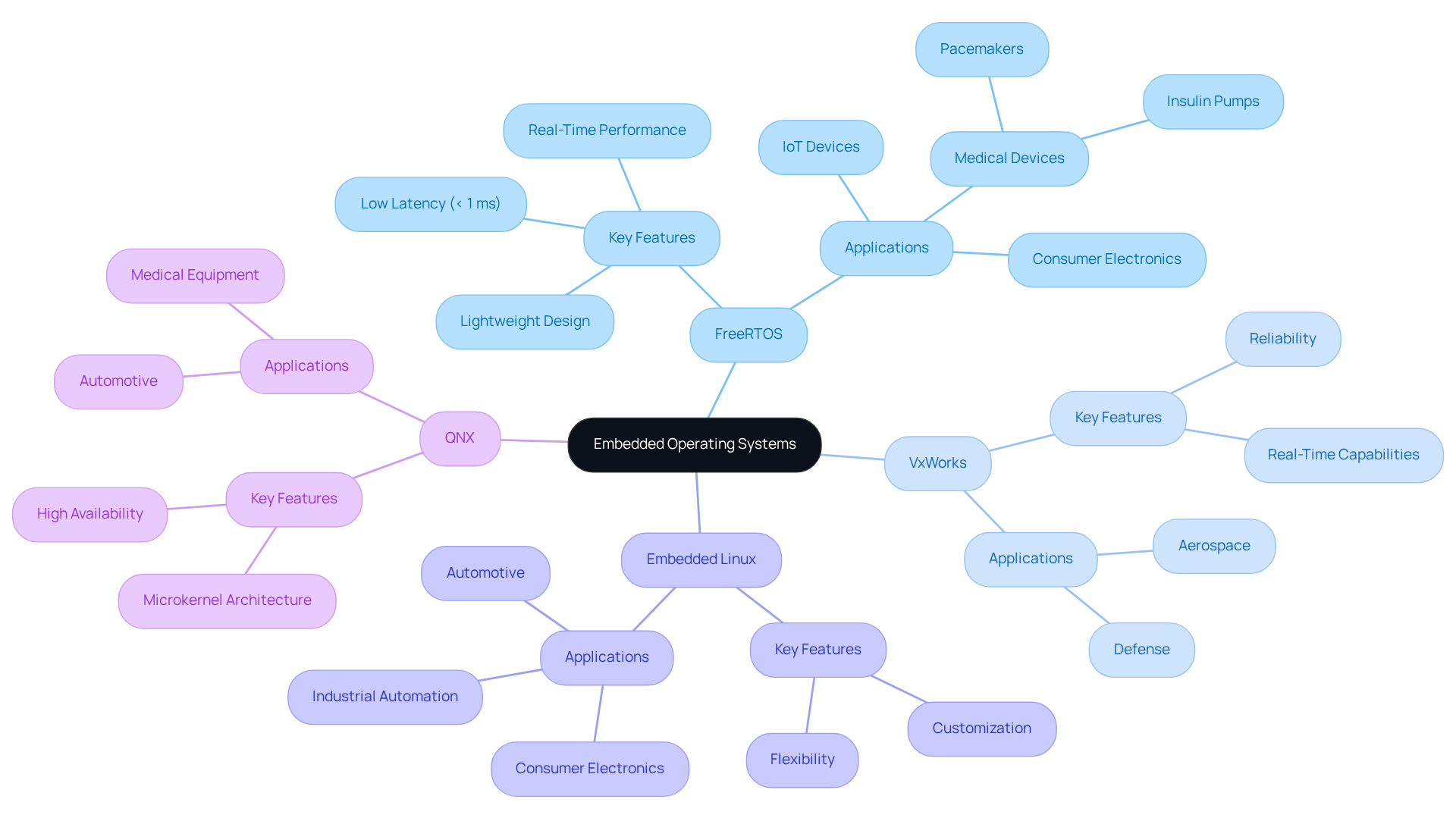
Embedded operating systems are essential across various industries, with several notable examples illustrating their impact:
FreeRTOS: This real-time operating system is widely used in microcontrollers for IoT devices, facilitating efficient task management and real-time performance. Its lightweight design enables low-latency capabilities, typically under 1 ms, making it ideal for applications that demand quick response times. As of 2026, FreeRTOS continues to be a preferred choice for IoT technologies, supporting a broad range of functionalities from smart home systems to medical applications, such as pacemakers and insulin pumps. Voler Systems enhances the performance of these devices by implementing AI-compatible design work to optimize power management, ensuring extended battery life and reliable operation even under demanding conditions.
VxWorks: Known for its reliability and real-time capabilities, VxWorks is primarily utilized in the aerospace and defense sectors. It supports critical applications, including military communication networks and navigation, where performance and safety are crucial. The platform's robust architecture ensures compliance with stringent safety standards, establishing it as a dependable solution for mission-critical environments. Voler Systems leverages VxWorks to develop solutions that meet these high standards while optimizing power consumption.
Embedded Linux: This versatile operating platform is extensively adopted in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and industrial automation. Its flexibility allows developers to tailor solutions for various applications, from infotainment systems in vehicles to automation controls in manufacturing. The embedded Linux market is projected to experience significant growth, reflecting its dominance within the developer community. Voler Systems employs Embedded Linux to create customized solutions that enhance functionality while managing power efficiency.
QNX: Frequently used in automotive and medical equipment, QNX is recognized for its robustness and real-time performance. Its microkernel architecture enhances reliability, making it suitable for applications that require high availability and safety. Voler Systems integrates QNX into its medical equipment solutions to ensure optimal performance and patient safety.
These examples illustrate what is an embedded OS and its integral role in enhancing the performance and reliability of modern devices, particularly in critical applications where precision and efficiency are paramount.
An embedded operating system functions as a specialized platform tailored for specific applications, particularly in environments where efficiency and real-time responsiveness are crucial. These operating systems play a vital role across various sectors, especially in healthcare, where they enhance the performance of devices such as medical monitoring instruments, ensuring reliable operation and adherence to stringent safety standards.
Key characteristics of embedded operating systems include:
The necessity of real-time operation is paramount, as many applications require immediate responses to external events. Additionally, the discussion explored various types of embedded operating systems, including:
Each type is designed to address the unique needs of different industries. Notable examples, such as FreeRTOS and VxWorks, exemplify the significant impact these systems have on modern technology.
In conclusion, the role of embedded operating systems is increasingly critical as industries evolve and demand more sophisticated, efficient, and reliable technological solutions. With the ongoing integration of AI and IoT, a comprehensive understanding of embedded operating systems will be essential for developers and businesses alike. Adopting these advanced systems not only fosters innovation but also ensures that devices can adapt to the ever-changing needs of users, particularly in vital fields like healthcare. The future of embedded operating systems is promising, and their continued advancement will be fundamental in shaping the landscape of modern technology.
What is an embedded operating system (OS)?
An embedded operating system is a specialized application designed to manage hardware and software resources in integrated devices, tailored for dedicated applications and often operating under real-time constraints.
How does an embedded OS differ from a general-purpose operating system?
Unlike general-purpose operating systems that cater to a wide range of tasks, an embedded OS is specifically designed for dedicated applications, optimizing performance and resource management for particular functions.
What are some key characteristics of integrated software solutions?
Key characteristics include optimized performance, efficient resource management, and enhanced reliability, ensuring that equipment operates effectively within their designated environments.
What industries are expected to increasingly adopt embedded operating systems?
Industries such as healthcare, automotive technologies, and consumer electronics are expected to increasingly adopt embedded operating systems.
What is the projected usage of integrated software platforms in healthcare by 2026?
It is projected that approximately 70% of healthcare equipment will utilize integrated software platforms by 2026.
Why are embedded operating systems crucial in healthcare technology?
Embedded operating systems are crucial in healthcare technology as they facilitate the seamless operation of devices like wearable sensors and heart pumps, which require precise control and immediate data processing.
What role do embedded operating systems play in the future of medical equipment?
As industries adopt advanced technologies, understanding embedded operating systems is expected to become crucial, making them indispensable for the future of medical equipment and beyond.
