What Is an Embedded OS? Importance and Key Characteristics Explained
Discover what is an embedded OS, its importance, characteristics, and applications in...

The rapid evolution of healthcare technology relies on innovative solutions that enhance patient care and streamline medical processes. Central to this transformation are IoT microcontrollers, which function as the brains of medical devices. They enable real-time data processing and communication, essential for effective health monitoring.
However, as the demand for sophisticated healthcare tools increases, so do the challenges of ensuring interoperability and security in an increasingly connected environment. The healthcare industry must leverage the potential of microcontrollers while navigating these complexities to drive meaningful advancements in medical device innovation.
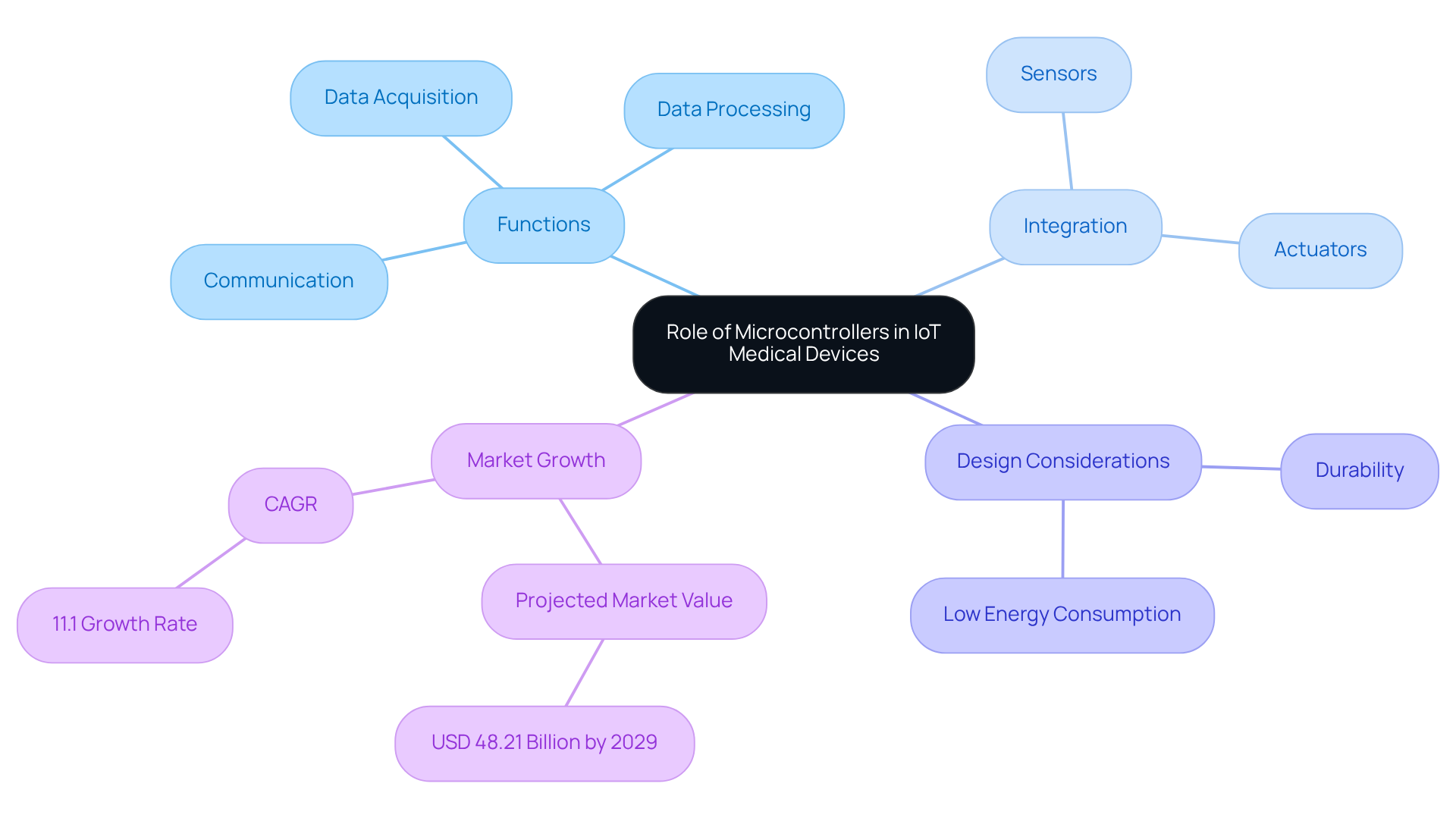
IoT microcontrollers play a pivotal role in IoT medical equipment, acting as the central processing units that enable essential functions such as data acquisition, processing, and communication. By integrating various components, including sensors and actuators, they support real-time monitoring of patient health metrics. For example, in wearable health monitors, these compact computing units efficiently process data from heart rate sensors and transmit this information to healthcare providers via wireless communication. This capability not only enhances patient monitoring but also facilitates timely interventions, significantly improving patient outcomes.
The design of these small computing units prioritizes low energy consumption, making them particularly suitable for battery-powered devices that demand durability and reliability. At Voler Systems, we specialize in the development of a diverse range of healthcare devices, including wearable technology, heart pumps, and liquid biopsy platforms, leveraging advancements in IoT microcontroller technology to optimize performance. Recent innovations, such as AI-driven analytics, have further augmented their capabilities for predictive health monitoring.
As a result, the microcontrollers market for health applications is projected to reach USD 48.21 billion by 2029, underscoring their growing importance in driving innovation within the field.
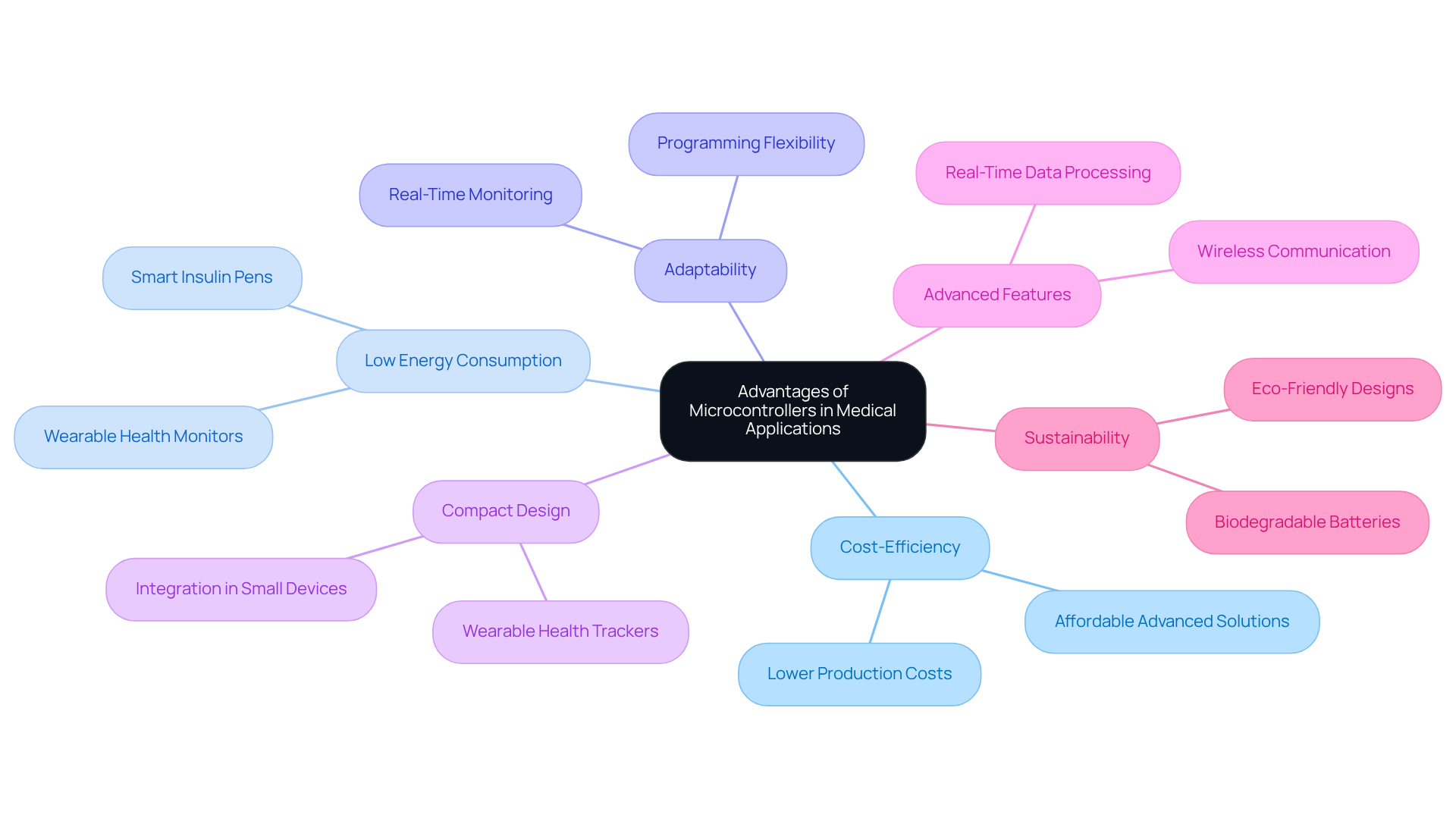
Microcontrollers play a pivotal role in advancing healthcare applications, primarily due to their numerous advantages. Their cost-efficiency enables manufacturers to produce high-quality products at lower price points, thereby making advanced medical solutions more accessible. For instance, the global medical microcontroller market was valued at USD 1.3 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 8.6% from 2024 to 2030. This growth underscores the increasing demand for sophisticated healthcare tools that leverage microcontroller technology. Additionally, the low energy consumption of these compact computing units is critical for battery-operated devices, allowing for extended operation without frequent recharging. Low-power chips are increasingly utilized in devices such as smart insulin pens and wearable health monitors, enhancing patient adherence and facilitating remote health management.
The adaptability of microcontrollers allows for programming across a spectrum of tasks, ranging from basic data collection to complex algorithms for real-time patient monitoring. Their compact design supports integration into small devices, such as innovative wearable health trackers, which are becoming more prevalent in patient care. Furthermore, the incorporation of advanced features like wireless communication and real-time data processing significantly enhances the functionality of healthcare instruments, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes. As the demand for integrated health solutions rises, driven by advancements in IoT technologies, the role of the IoT microcontroller in health innovation becomes increasingly essential. Manufacturers are also prioritizing environmentally sustainable designs and materials, thereby reducing the ecological footprint of healthcare equipment, which aligns with the growing focus on sustainability in health services.
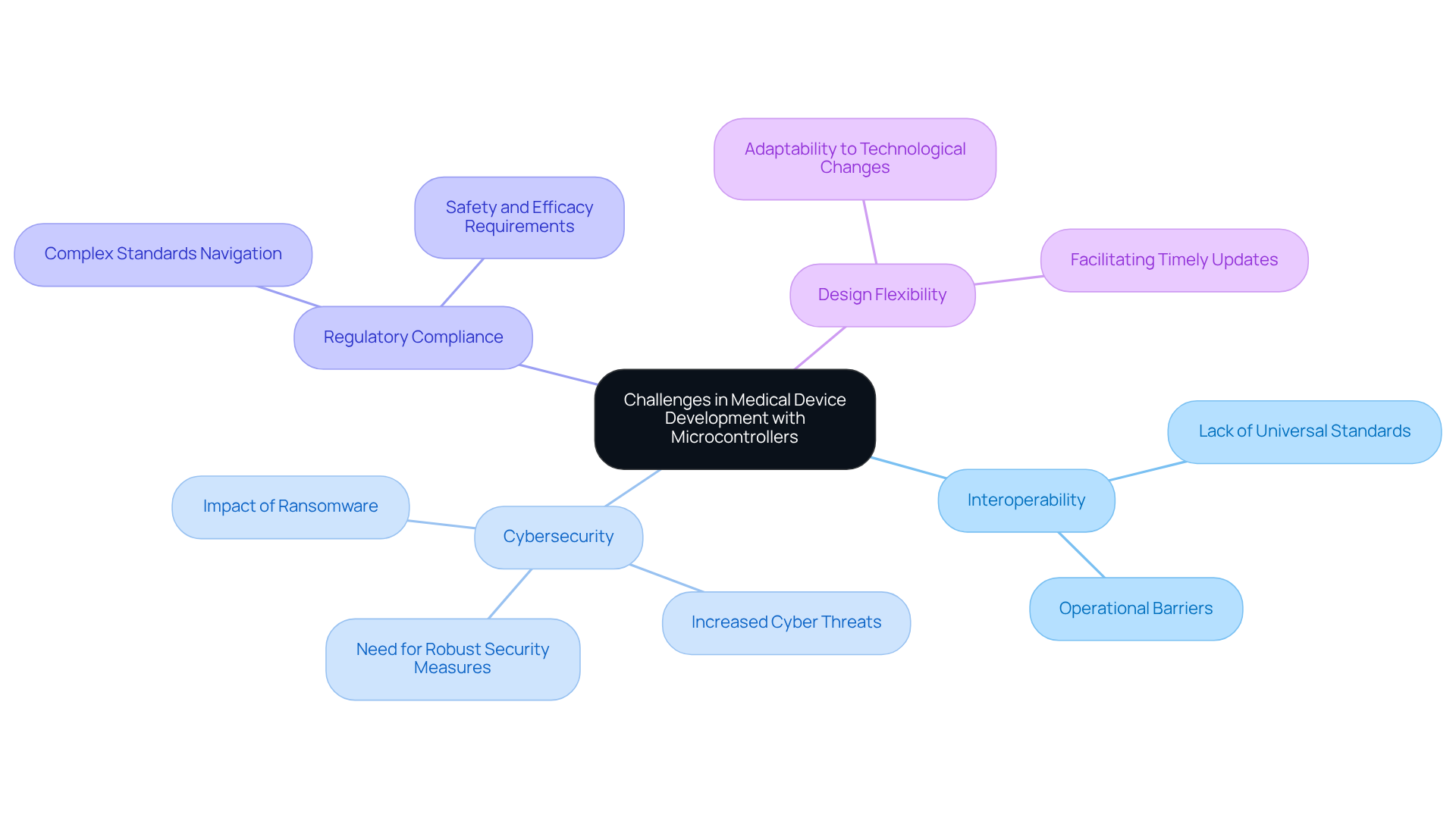
Incorporating microcontrollers into healthcare instruments offers numerous benefits, yet it also presents significant challenges that must be addressed. A primary concern is ensuring interoperability among various equipment and systems, which is crucial for seamless communication in IoT environments. Notably, 92% of healthcare organizations reported experiencing at least one cyberattack in the past year, highlighting the increasing cybersecurity threats associated with connected medical devices. As these tools become more interconnected, robust security measures are imperative to safeguard sensitive patient information.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance poses an additional challenge, as developers must navigate complex standards to ensure their products meet safety and efficacy requirements. The rapid pace of technological advancement can also lead to obsolescence, necessitating flexible design strategies that facilitate timely updates and improvements. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort among engineers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare professionals to ensure that microcontroller-based systems are effectively developed and utilized, ultimately enhancing patient care and safety.
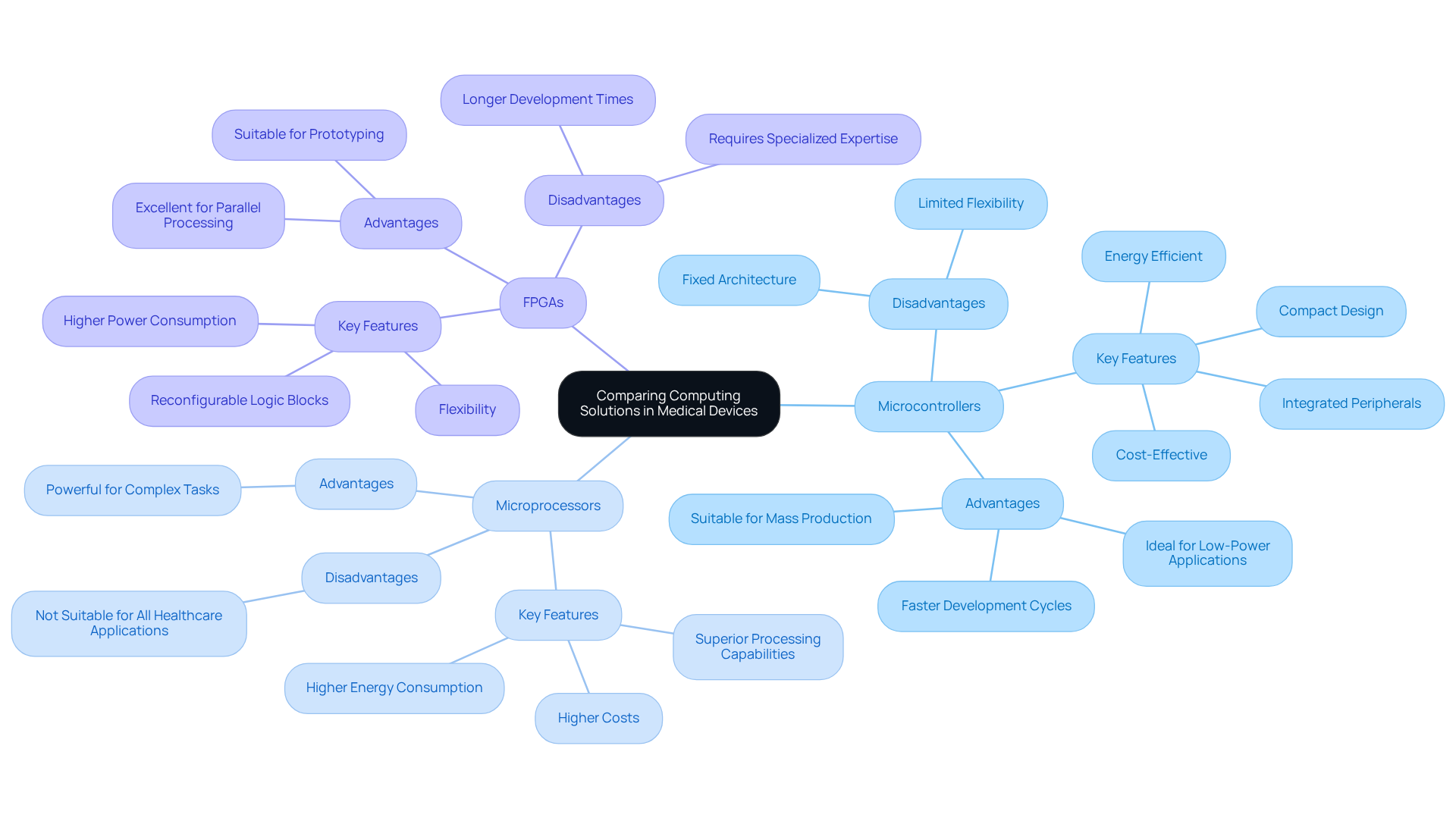
In the field of healthcare technology innovation, IoT microcontrollers distinguish themselves from other computing solutions, such as microprocessors and FPGAs. Their cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency make them particularly suitable for low-power health equipment that demands extended battery life. While microprocessors offer superior processing capabilities, they come with higher costs and energy consumption, which may not align with the requirements of all healthcare applications. Conversely, FPGAs, recognized for their flexibility and capacity to handle complex tasks, often require longer development times and specialized expertise, potentially impeding rapid prototyping efforts.
Microcontrollers, in contrast, are engineered with integrated peripherals that simplify the design process, enabling faster development cycles. This advantage is critical for startups and smaller companies aiming to innovate in the medical equipment sector by leveraging an IoT microcontroller without incurring substantial costs or delays. For example, the compact design of small computing devices is advantageous for portable applications, facilitating efficient use of space and resources.
Moreover, small computing units consume significantly less energy than FPGAs, making them ideal for battery-powered equipment. This energy efficiency is particularly vital in medical applications, where devices must operate reliably over extended periods without frequent recharging. Additionally, environmental factors such as moisture and temperature can greatly affect the performance and longevity of wearable sensors, a consideration that Voler Systems incorporates into its designs. As the market for IoT microcontrollers continues to expand, propelled by advancements in healthcare infrastructure and a growing demand for smart medical devices, the significance of microcontrollers in driving innovation is undeniable.
The significance of IoT microcontrollers in medical device innovation is paramount. These compact yet powerful units form the backbone of modern healthcare technology, enabling real-time data processing, seamless communication, and enhanced patient monitoring. As the healthcare industry evolves, the reliance on microcontrollers for developing smarter, more efficient medical devices becomes increasingly evident.
Key points throughout this discussion highlight the advantages of microcontrollers, including:
These features not only facilitate the creation of advanced medical solutions but also address critical challenges such as interoperability and cybersecurity. Moreover, a comparison with alternative computing solutions underscores the unique position of microcontrollers as the preferred choice for many medical applications, particularly regarding efficiency and ease of integration.
As the healthcare landscape progresses, embracing the potential of IoT microcontrollers will be essential for driving innovation and improving patient outcomes. Stakeholders in the medical field - manufacturers, engineers, and healthcare professionals - must collaborate to harness these technologies effectively, ensuring robust and secure medical devices that meet the needs of patients and providers alike. The future of healthcare technology lies in the continued advancement and integration of microcontroller capabilities, paving the way for a more connected and efficient healthcare system.
What is the role of microcontrollers in IoT medical devices?
Microcontrollers serve as the central processing units in IoT medical equipment, enabling functions such as data acquisition, processing, and communication.
How do microcontrollers enhance patient monitoring?
They integrate various components like sensors and actuators to support real-time monitoring of patient health metrics, allowing for efficient data processing and transmission to healthcare providers.
What are some examples of devices that utilize IoT microcontrollers?
Examples include wearable health monitors, heart pumps, and liquid biopsy platforms.
Why is low energy consumption important for microcontrollers in medical devices?
Low energy consumption is crucial for battery-powered devices, ensuring durability and reliability in continuous health monitoring.
How have recent innovations improved the capabilities of microcontrollers in healthcare?
Innovations such as AI-driven analytics have enhanced microcontrollers' capabilities for predictive health monitoring.
What is the projected market value for microcontrollers in health applications by 2029?
The microcontrollers market for health applications is projected to reach USD 48.21 billion by 2029.
