4 Key Topics in Embedded Systems for Medical Device Success
Explore essential topics in embedded systems for successful medical device development...
Embedded operating systems (EOS) play a critical role in the functionality of numerous devices, especially within the medical sector. As the demand for smart, connected healthcare solutions continues to rise, it is essential to grasp the importance of these specialized systems in ensuring patient safety and device reliability. However, how do these tailored software platforms effectively balance complex tasks with the stringent regulatory requirements inherent in an industry where precision is vital?
A built-in software (EOS) is specialized code designed to manage hardware resources and provide a foundation for running applications in integrated systems. Unlike general-purpose platforms that cater to a broad range of tasks, specialized software is tailored for specific functions within devices, including medical apparatus, automotive technologies, and consumer electronics. These systems are optimized for performance, reliability, and efficiency, often operating under constraints such as limited processing power and memory.
Notable examples of integrated software environments include:
The growth of integrated software in medical equipment is particularly significant, with the market projected to reach $19,519.09 million by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.65% from 2023 to 2030. This expansion is fueled by the increasing demand for smart, connected, and secure IoT-enabled medical devices, highlighting the essential role of embedded operating systems in effective hardware resource management and enhanced functionality.
Voler Systems provides comprehensive IoT design consulting, addressing challenges in sensor integration, power management, and security-key factors in improving battery life for wireless medical devices. Additionally, Voler Systems leverages AI technologies to enhance the functionality and security of connected medical equipment, ensuring they adapt to the evolving needs of healthcare applications. Safety in connected medical devices is paramount, as it ensures confidentiality, data integrity, and authentication, which brings to light what is embedded OS and its crucial role in maintaining trust in medical applications.
What is embedded OS plays a crucial role in the functionality of modern medical equipment, particularly in facilitating real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and treatment. These frameworks ensure that devices operate reliably under stringent regulatory standards, which is essential for patient safety. As Rachel Cashman notes, 'What is embedded OS is the function of embedded technologies as the brains of diagnostic apparatus, ensuring real-time processing and analysis of medical data.' For instance, in devices such as insulin pumps and heart monitors, integrated software manages vital functions including data collection, processing, and communication with healthcare providers.
Moreover, these platforms enable the incorporation of advanced features like wireless connectivity and data analytics, which illustrates what is embedded OS in significantly enhancing the effectiveness of medical technologies. The transition from connected technologies to truly wireless solutions exemplifies the innovative advancements in cardiac monitoring, demonstrating how integrated devices can support continuous tracking of vital signs. Additionally, the development of novel calf-worn devices for motion and circumference tracking in rehabilitation showcases the adaptability of integrated frameworks in meeting medical equipment standards.
The ability to perform specialized tasks efficiently positions integrated software as a cornerstone of innovation across various technological domains. As the field of in vitro diagnostics evolves, the significance of integrated technologies becomes increasingly pronounced, ensuring that diagnostic devices deliver rapid and accurate results, thereby improving overall healthcare delivery.
To understand what is embedded os, one can classify embedded operating platforms based on their functionality and application, particularly within the healthcare sector. The primary classifications include:
Real-Time Operating Environments (RTOS): These platforms are designed to process data as it arrives, ensuring timely responses to external events. Their importance is underscored in medical instruments that monitor vital signs, where prompt action is critical. The RTOS market is projected to experience significant growth, with North America anticipated to capture a 35% share by 2035, driven by advancements in autonomous vehicles and healthcare applications.
Single-Task Operating Environments: These systems are tailored to perform a specific task, making them ideal for simple devices such as basic medical sensors or alarms. Their straightforward design facilitates efficient operation in contexts where complex processing is unnecessary.
Multi-Tasking Operating Environments: These platforms enable the simultaneous execution of multiple tasks, which is vital for advanced devices like wearable health monitors that track various metrics concurrently. This capability enhances both functionality and user experience in health monitoring tools.
Networked Operating Environments: These platforms facilitate interaction among devices over networks, promoting data sharing and remote monitoring - an increasingly vital aspect of IoT applications. The integration of interconnected software in healthcare devices significantly improves patient care through enhanced data accessibility and real-time monitoring.
The selection of an integrated software platform is contingent upon the specific requirements of the application, including what is embedded os, processing capability, memory constraints, and the necessity for real-time performance. As the healthcare sector evolves, the role of integrated software, particularly RTOS, will be pivotal in advancing medical technology and enhancing patient outcomes.
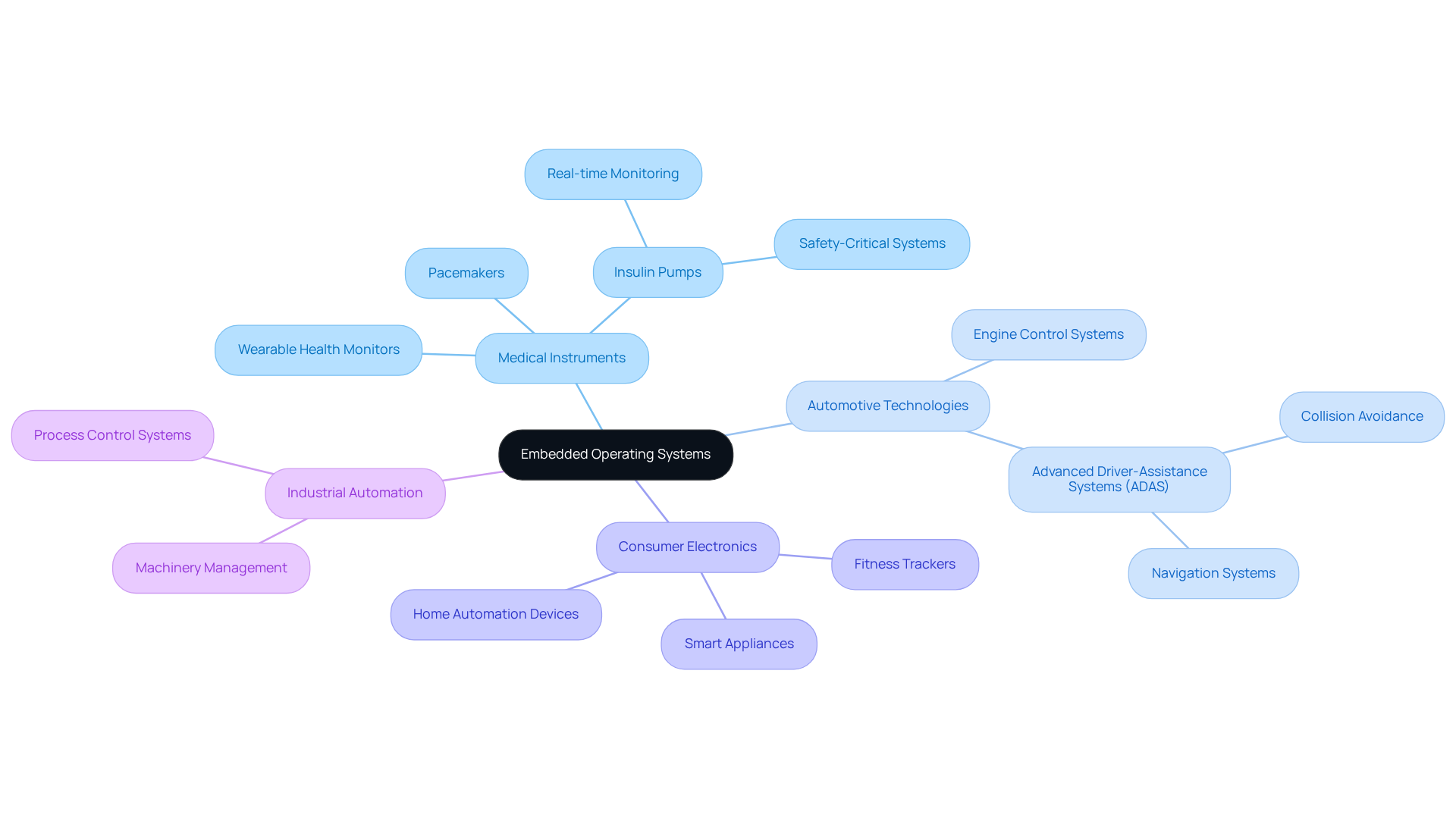
Embedded software plays a critical role across a variety of applications, particularly within the medical sector. Key applications include:
Medical Instruments: Essential devices such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, and wearable health monitors utilize integrated operating platforms for real-time data processing and patient monitoring. This ensures timely and accurate health interventions. Voler Systems specializes in developing a range of medical devices, including wearable technology and heart pumps, employing AI-assisted engineering to ensure these solutions are both reliable and designed for the future of intelligent healthcare, all while adhering to documentation compliance standards.
Automotive Technologies: In the automotive industry, integrated technologies oversee vital functions such as engine control, navigation, and safety features, significantly enhancing both performance and safety. For example, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) utilize these technologies to improve collision avoidance and overall vehicle reliability.
Consumer Electronics: Smart appliances, fitness trackers, and home automation devices leverage integrated software to deliver user-friendly interfaces and seamless connectivity, making everyday tasks more efficient and enjoyable.
Industrial Automation: Within manufacturing, integrated technologies are essential for managing machinery and processes, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.
These varied applications underscore the adaptability and vital role of integrated operating environments, highlighting what is embedded os in fostering innovation and enhancing functionality across multiple sectors, particularly in healthcare, where accuracy and reliability are paramount. For instance, the control software for a personal insulin pump is engineered to replicate the pancreas's function, ensuring consistent insulin delivery and highlighting what is embedded os in health management. Voler Systems' expertise in electronic design services accelerates the development of wearable and IoT solutions, optimizing battery life and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Embedded operating systems (EOS) are fundamental to the advancements in modern technology, especially in the medical field, where precision and reliability are critical. These specialized systems manage hardware resources and enable real-time data processing, significantly enhancing the functionality of essential healthcare applications. This ensures that medical devices operate both efficiently and safely.
The article underscores the importance of embedded operating systems from multiple perspectives. Key insights include:
The anticipated growth of the embedded OS market within the medical sector highlights the rising demand for smart, connected devices that prioritize patient safety and effective data management.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, the importance of embedded operating systems becomes increasingly evident. They not only foster innovation but also enhance patient care through improved device functionality and security. For stakeholders in the medical field, embracing advancements in embedded technology is crucial to remain at the forefront of delivering safe, efficient, and reliable healthcare solutions. The imperative is clear: investing in and comprehending the role of embedded operating systems is essential for anyone involved in the development and implementation of medical technologies.
What is an embedded operating system (EOS)?
An embedded operating system is specialized software designed to manage hardware resources and provide a foundation for running applications in integrated systems. It is tailored for specific functions within devices, such as medical apparatus, automotive technologies, and consumer electronics.
How does an embedded operating system differ from a general-purpose operating system?
Unlike general-purpose operating systems that cater to a wide range of tasks, embedded operating systems are optimized for performance, reliability, and efficiency in specific applications, often operating under constraints like limited processing power and memory.
Can you provide examples of embedded operating systems?
Notable examples of embedded operating systems include FreeRTOS, VxWorks, and various customized Linux distributions designed to meet the unique requirements of specific applications.
What is the projected market growth for embedded operating systems in medical equipment?
The market for embedded operating systems in medical equipment is projected to reach $19,519.09 million by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.65% from 2023 to 2030.
What factors are driving the growth of embedded operating systems in medical devices?
The growth is fueled by the increasing demand for smart, connected, and secure IoT-enabled medical devices, highlighting the essential role of embedded operating systems in managing hardware resources and enhancing functionality.
What role does Voler Systems play in the development of embedded operating systems for medical devices?
Voler Systems provides comprehensive IoT design consulting, addressing challenges in sensor integration, power management, and security, which are key factors in improving battery life for wireless medical devices. They also leverage AI technologies to enhance the functionality and security of connected medical equipment.
Why is safety important in connected medical devices?
Safety is paramount in connected medical devices to ensure confidentiality, data integrity, and authentication, which are crucial for maintaining trust in medical applications.
