The wireless standard you select for your IoT device can greatly influence its performance, usability, security, and reliability. To pinpoint the best-fit standard for your IoT device, you must first determine its application. What IoT device are you developing and what is it for?
Specify device application.
Knowing the purpose of your device can help you determine the key requirements for building it, such as how much power it needs to operate efficiently, how fast it should be able to transmit data, and what type of wireless or wired network it should use.
If you are building a device for remote patient monitoring, for example, you need to choose a wireless standard that provides you the right mix of low power consumption for long periods of time as well as real-time, fast, and long-distance transmission of healthcare data, which may be particularly crucial in emergencies.
Determine how much power your device needs.
Different wireless standards require very different levels of power. The required power depends on the data rate and range of transmission. For example, referring to the table below, your device may require 100 mW of power to transmit 120 bytes of data per second one kilometer using LTE Cellular. But using Bluetooth LE to transmit 1 meter, it may only need 0.15 mW of power.
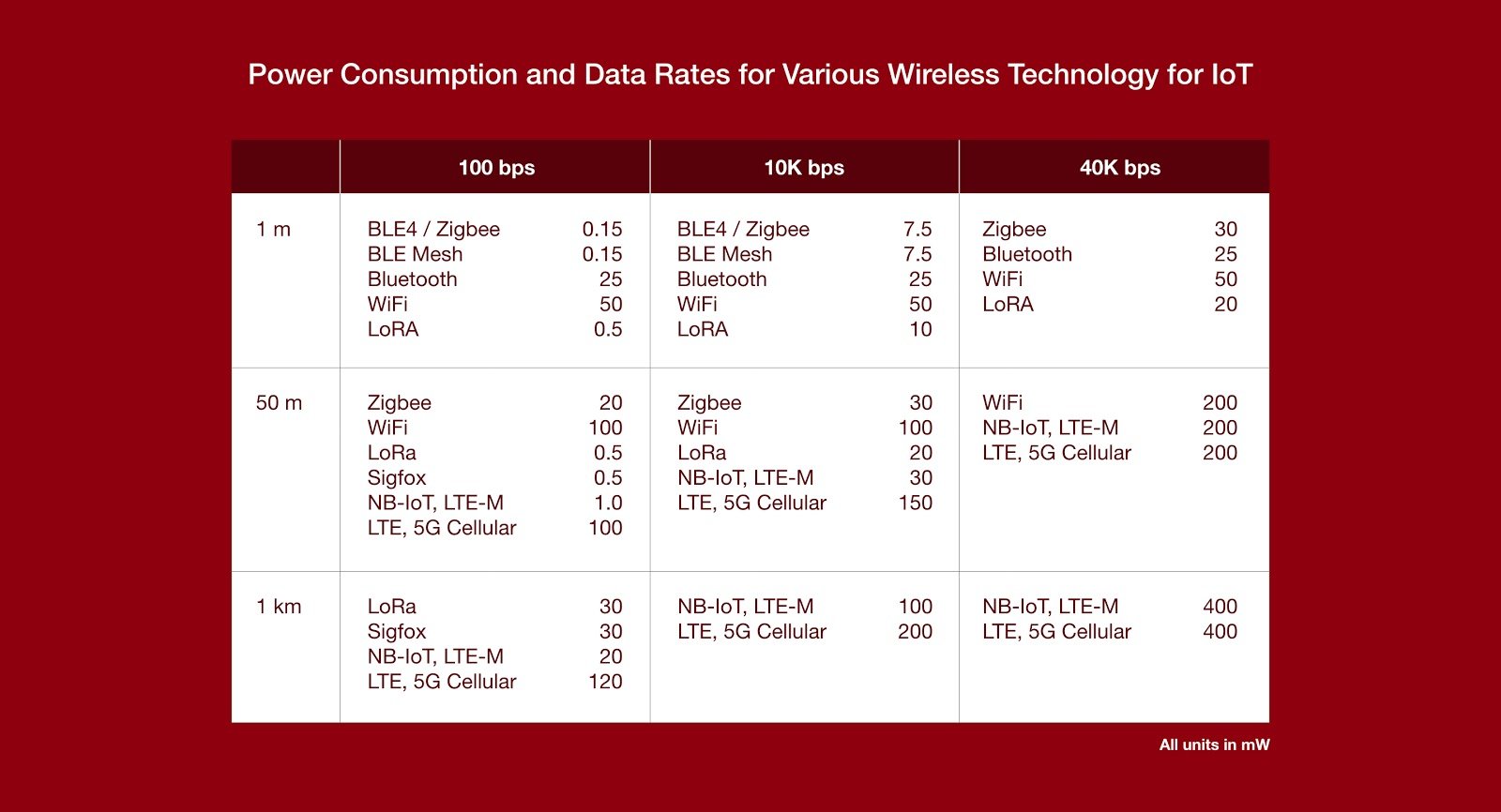
Based on your device application, determine how far and how fast it should be able to transmit data.
If your device is required only to transmit data as far as 10 meters, BLE and Bluetooth sensors can be sufficient. But IoT devices for industrial and commercial purposes such as inventory management or for wearable devices for health monitoring may require sensors with a higher working range such as NB-IoT or LoRa WAN.
Cellular wireless protocols, on the other hand, allow your IoT devices to transmit data to far locations. The same is true for SigFox, which can transmit data as far as 50 kilometers. But unlike cellular standards that have a high data rate, SigFox can only transmit 300 bits of data per second.
Know what type(s) of data it can support.
Say you are developing an IoT device that should be able to transmit videos. SigFox, Bluetooth, and Zigbee will not work, because they do not support this high data rate. Wi-Fi and Cellular transmit full HD video, voice, and text. SigFox would be excellent for transmitting only text, and Bluetooth and Zigbee can transmit audio, but the distance is very limited.
Look at other deciding factors such as cost, network topology, and operating frequency.
Most wireless standards are inexpensive, but some (like Zigbee) may be costly to implement. Network topology and operating frequency are also important factors because they determine power consumption and performance.
Conclusion
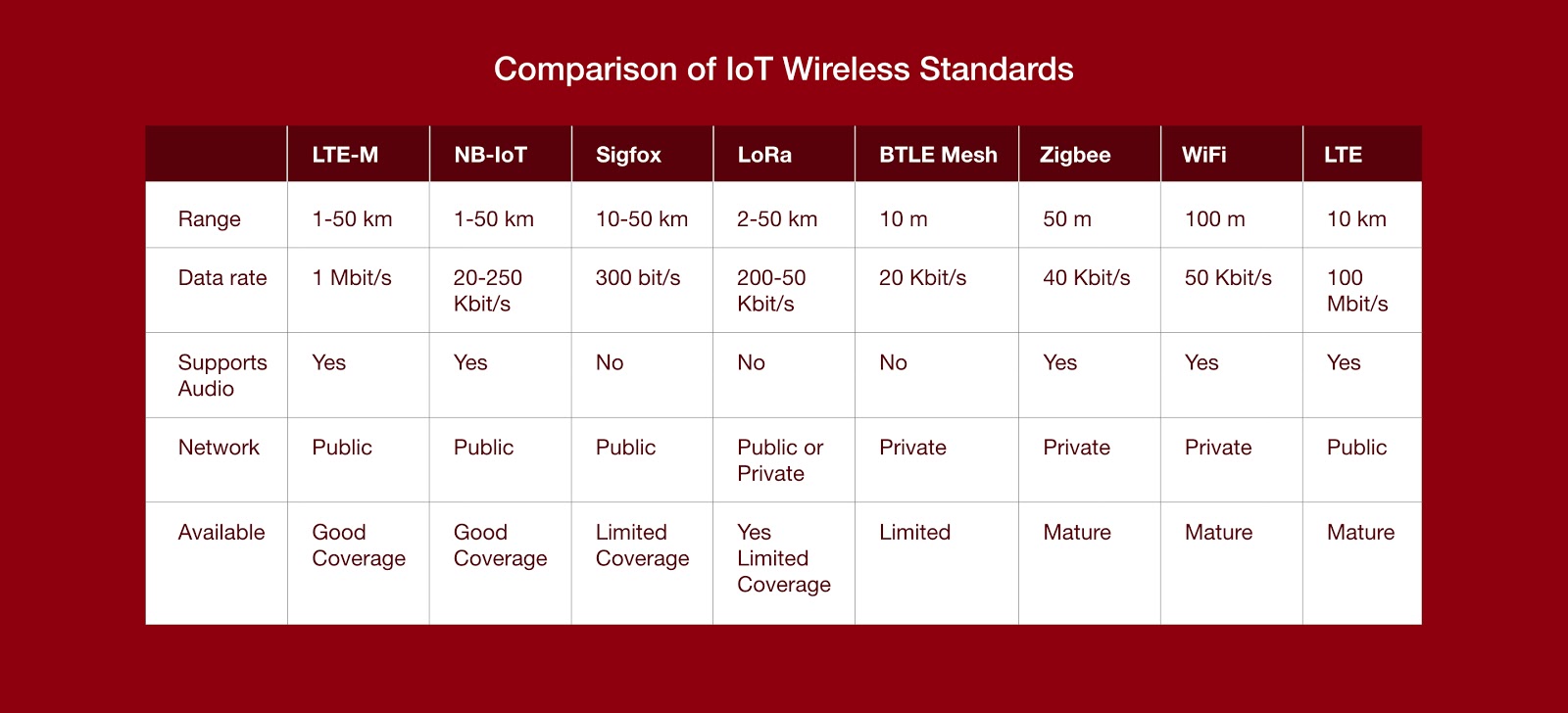
Choosing the right wireless standard can be very tricky. You may refer to the table below when choosing a wireless standard for your IoT device. The table lists the common wireless standards used for IoT devices, along with their characteristics.
Our team of IoT device development experts can guide you through choosing the right wireless standard for your IoT machines. Contact an IoT expert now to learn more about choosing the right wireless standard for your IoT device.