4 Key Topics in Embedded Systems for Medical Device Success
Explore essential topics in embedded systems for successful medical device development...
Operating systems play a crucial role in embedded systems, serving as the backbone for numerous applications across vital industries. As advanced technologies continue to evolve in sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and consumer electronics, the selection of an appropriate embedded operating system has emerged as a critical decision for developers. This choice directly impacts performance and reliability. However, the vast array of options available can be overwhelming.
What factors should developers consider to determine the best fit for specific applications? This article explores best practices for selecting an operating system in embedded systems, providing insights into essential selection criteria, the advantages and disadvantages of popular systems, and real-world applications that highlight their significance.
An operating system in embedded systems is specialized software designed to manage hardware resources and provide a foundation for application software within integrated systems. Unlike general-purpose operating platforms, these specialized operating systems in embedded systems are designed for specific tasks, thereby enhancing performance and optimizing resource usage. Their importance is particularly evident in sectors such as healthcare, automotive systems, and consumer electronics, where reliability and efficiency are paramount.
In healthcare equipment, for example, an integrated OS plays a critical role in ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards, which in turn enhances patient safety and device efficiency. The global integrated software market, valued at USD 17.9 billion in 2024, is projected to grow to USD 30.2 billion by 2030, reflecting a robust annual growth rate of nearly 9.5%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for advanced healthcare technologies, where integrated frameworks are essential for facilitating real-time data processing and improving patient outcomes.
Recent advancements, particularly in Linux integrated systems, have significantly transformed healthcare devices by enhancing connectivity and security. These improvements enable functionalities such as remote monitoring and real-time data analysis. For instance, Voler Technologies has successfully integrated circuits into healthcare applications, including wearable ECG monitors that continuously evaluate heart rhythms and alert healthcare providers to potential risks, thus enabling timely interventions.
As the market continues to evolve, the importance of selecting the appropriate operating system in embedded systems becomes increasingly critical for manufacturers aiming to deliver reliable and efficient health solutions.
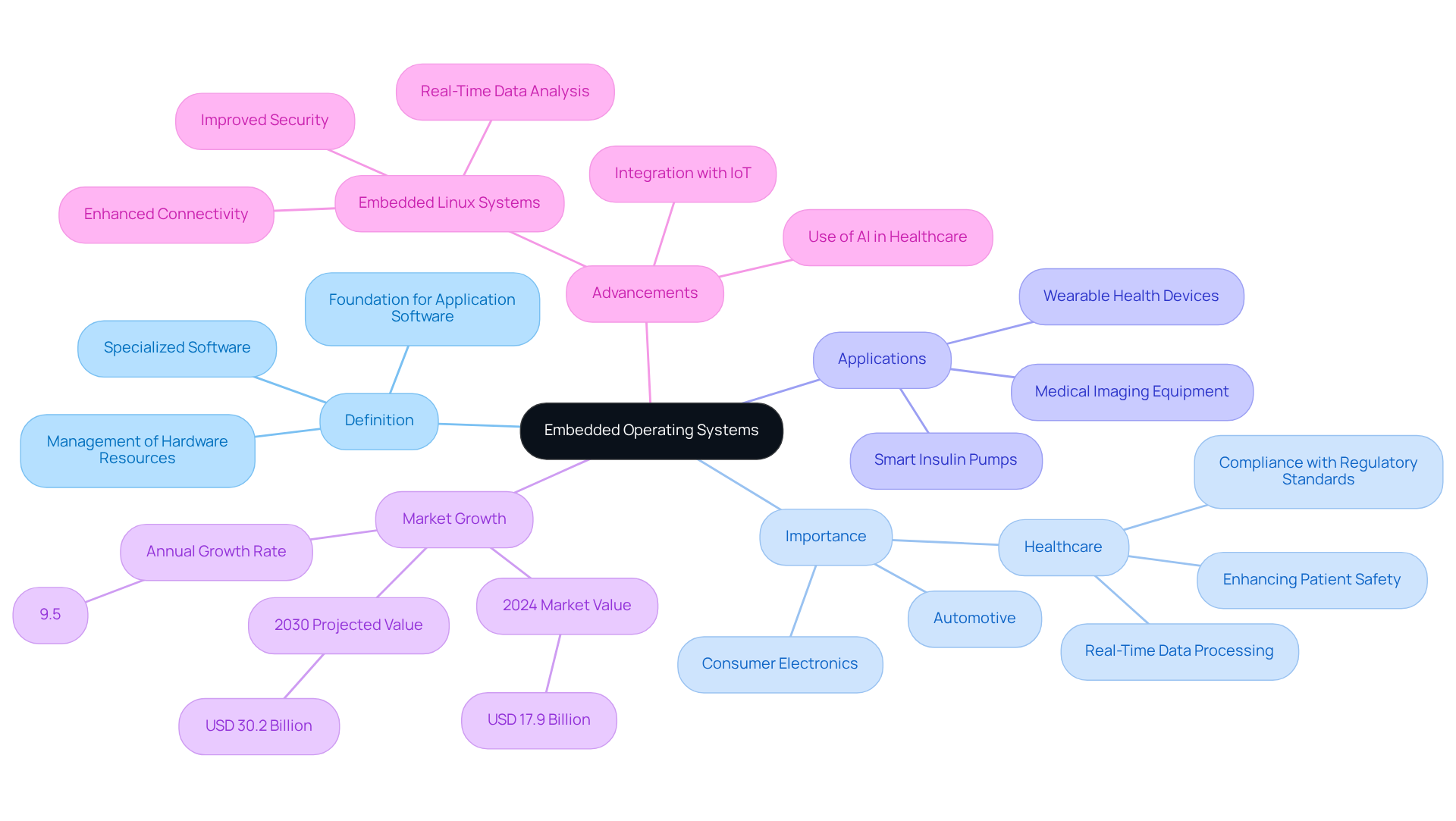
Selecting the appropriate embedded operating system (OS) is critical for the success of medical devices, necessitating a thorough evaluation of several key criteria:
Hardware Compatibility: The OS must support the specific hardware components of the device. This compatibility is essential for seamless integration and optimal performance. For instance, setups utilizing microcontrollers or complex SoCs require careful alignment of the OS with hardware capabilities to avoid performance bottlenecks.
Performance Requirements: It is vital to assess the processing power and memory needs of the application. Medical instruments can range from basic 8-bit microcontrollers to advanced systems with high processing capabilities. Understanding these requirements aids in selecting an operating system in embedded system that can efficiently manage resources without compromising functionality.
Real-Time Capabilities: Many healthcare applications demand real-time processing, which may necessitate a real-time operating system (RTOS). An RTOS is particularly beneficial for systems requiring deterministic behavior, ensuring prompt responses to critical events, such as in surgical instruments where delays can result in severe consequences.
Development Resources: The availability of development tools and community support for the OS can significantly influence the development timeline. An operating system in embedded system with a robust ecosystem can facilitate quicker development and troubleshooting, which is essential in the fast-paced healthcare device industry.
Security Features: Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, evaluating the OS's security protocols is paramount. Features such as secure boot, data encryption, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA are critical for protecting patient information and maintaining trust.
Cost and Licensing: Analyzing the financial implications of using a commercial versus open-source OS is necessary. While open-source options like FreeRTOS and Zephyr RTOS offer flexibility and lower costs, commercial solutions may provide enhanced support and features that justify their expense.
By carefully considering these factors, developers can select an operating system in embedded system that not only meets technical requirements but also aligns with budgetary constraints and project timelines. Furthermore, with the emergence of Edge AI, developers should contemplate how these advanced features can enhance the functionality of integrated platforms, potentially influencing the selection criteria for operating environments. Statistics indicate that hardware compatibility issues are a leading cause of project delays, underscoring the importance of thorough evaluation in the selection process.
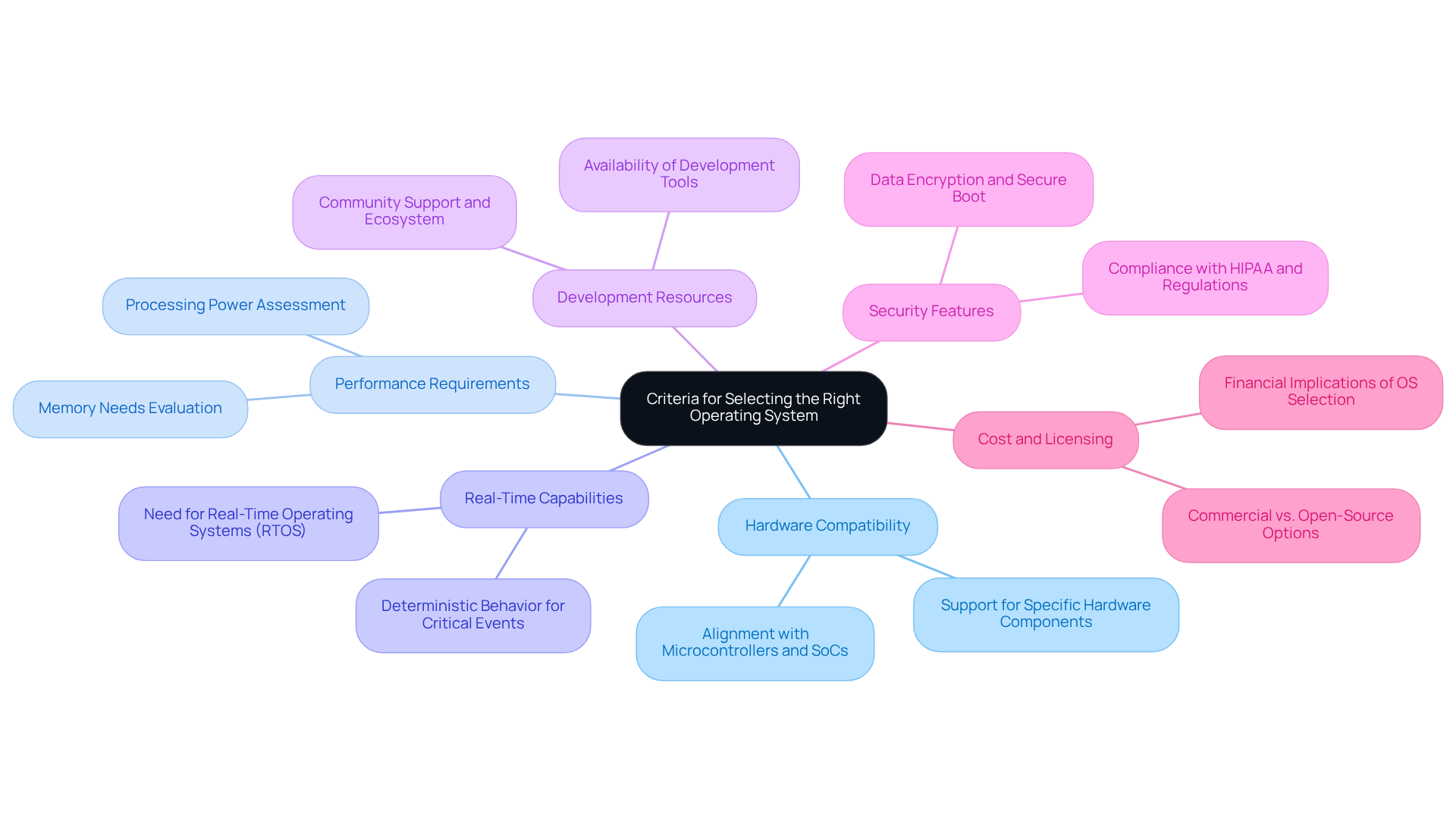
Several popular embedded operating systems are widely utilized in the industry, each presenting distinct advantages and disadvantages, particularly concerning battery life optimization and AI integration in medical devices:
FreeRTOS:
Embedded Linux:
VxWorks:
Zephyr:
Understanding these advantages and disadvantages allows developers to align their project requirements with the features of the operating system in embedded systems, particularly in enhancing battery life and integrating AI technologies, as illustrated by Voler Systems' approach.
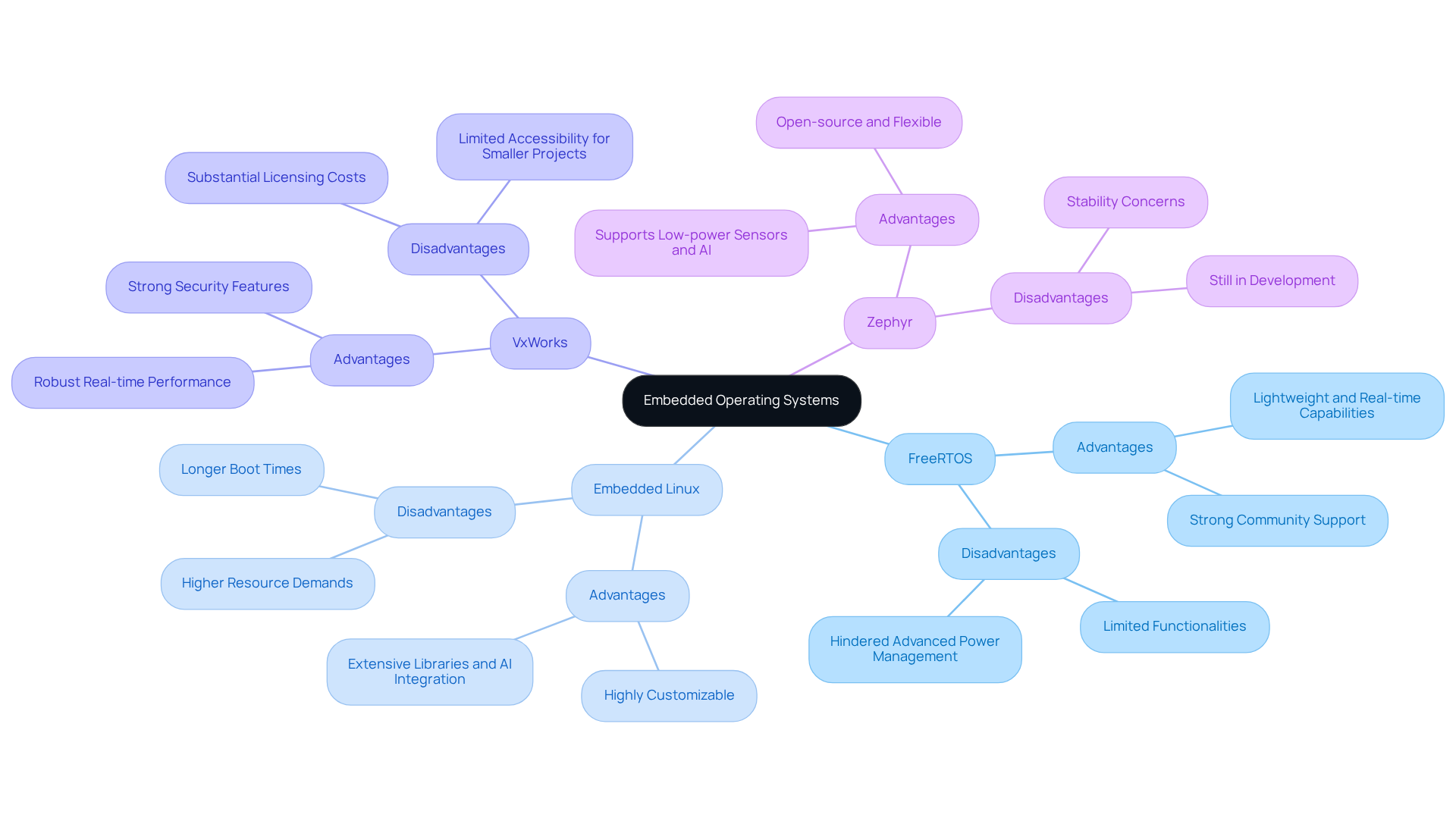
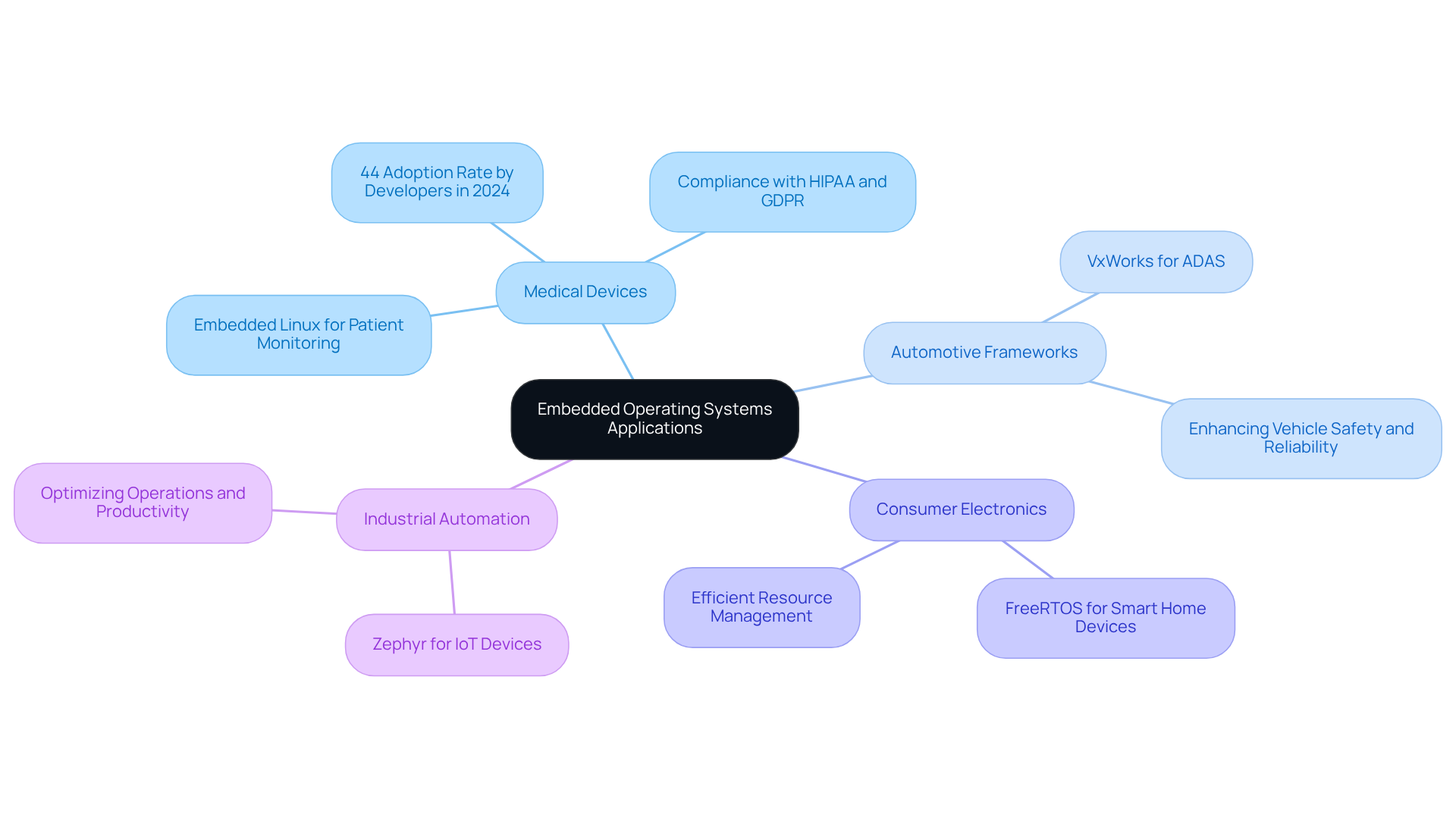
The operating system in embedded systems is integral to a diverse range of applications across multiple industries. For example:
Medical Devices: Embedded Linux is widely utilized in imaging devices and patient monitoring solutions, offering the flexibility necessary for complex applications. Its robust security features are critical for safeguarding sensitive patient data, ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. In 2024, it is anticipated that 44% of developers will adopt Embedded Linux for these applications, highlighting its prominence in the medical sector.
Automotive Frameworks: Real-time operating frameworks like VxWorks are vital in advanced driver-assistance technologies (ADAS), where immediate responses to safety functions are essential. The integration of these systems enhances vehicle safety and reliability, addressing the increasing demand for automated driving technologies.
Consumer Electronics: FreeRTOS is a favored choice for many smart home devices, providing efficient resource management and real-time capabilities. Its lightweight design facilitates seamless integration into various consumer electronics, contributing to the proliferation of smart technology in daily life.
Industrial Automation: Zephyr is gaining popularity in IoT devices for smart factories, enabling smooth communication between machines and cloud services. This functionality is crucial for optimizing operations and boosting productivity in industrial environments.
These examples illustrate how the choice of an operating system in embedded systems can significantly influence the performance, reliability, and functionality of devices in practical applications, particularly in sectors where precision and security are paramount.
Selecting the appropriate operating system for embedded systems is a critical decision that can greatly impact the performance and reliability of various applications. The specialized nature of embedded operating systems, designed for specific tasks, highlights their significance across essential sectors such as healthcare, automotive, and consumer electronics. As technology evolves, grasping the intricacies of these operating systems becomes crucial for developers striving to create efficient and reliable solutions.
In examining best practices for choosing an embedded operating system, several key criteria have surfaced:
Furthermore, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of popular operating systems like FreeRTOS, Embedded Linux, VxWorks, and Zephyr can assist developers in aligning their project requirements with suitable technological solutions. Real-world applications further demonstrate how these systems enhance device functionality and security, underscoring their essential role in contemporary technology.
Given the rapid advancement of embedded systems, it is imperative for developers to remain updated on the latest trends and best practices in operating system selection. As the market expands and the demand for sophisticated technologies rises, making informed decisions will not only optimize device performance but also ensure adherence to regulatory standards and enhance user safety. Adopting a strategic approach to selecting an operating system will ultimately foster innovations that can transform industries and elevate everyday life.
What are embedded operating systems?
Embedded operating systems are specialized software designed to manage hardware resources and provide a foundation for application software within integrated systems, focusing on specific tasks to enhance performance and optimize resource usage.
Why are embedded operating systems important?
They are crucial in sectors such as healthcare, automotive systems, and consumer electronics, where reliability and efficiency are essential. They ensure compliance with regulatory standards, enhance patient safety, and improve device efficiency.
How is the global integrated software market projected to grow?
The global integrated software market, valued at USD 17.9 billion in 2024, is projected to grow to USD 30.2 billion by 2030, reflecting an annual growth rate of nearly 9.5%.
What factors are driving the growth of embedded operating systems in healthcare?
The increasing demand for advanced healthcare technologies and the need for integrated frameworks to facilitate real-time data processing and improve patient outcomes are key factors driving growth.
What advancements have been made in Linux integrated systems?
Recent advancements have enhanced connectivity and security in healthcare devices, enabling functionalities such as remote monitoring and real-time data analysis.
Can you provide an example of an application of embedded operating systems in healthcare?
An example is the integration of circuits into wearable ECG monitors that continuously evaluate heart rhythms and alert healthcare providers to potential risks, allowing for timely interventions.
Why is selecting the appropriate operating system critical for manufacturers?
Choosing the right operating system is increasingly important for manufacturers to deliver reliable and efficient health solutions as the market continues to evolve.
