The Parts Supply Crisis: Understanding Tech's Biggest Challenge Yet
Anyone in the tech industry knows that we're in a global supply crunch. It's an issue...
Embedded operating systems serve as the backbone of contemporary technology, quietly enabling devices that perform essential functions across various sectors, particularly in healthcare and the Internet of Things (IoT). As these specialized systems advance, they deliver unmatched efficiency and reliability, ensuring that critical devices, such as pacemakers and smart appliances, function without interruption.
However, with the rapid pace of technological advancements and increasing system complexity, industries face the challenge of fully leveraging the capabilities of embedded operating systems while ensuring safety and optimal performance.
This article examines the definition, importance, and practical applications of embedded operating systems, highlighting their significant influence on technology and society.
An integrated software framework serves as a specialized tool for managing hardware and software resources in dedicated devices, which are designed to perform specific tasks. Unlike general-purpose software platforms, specialized operating systems (OSs) are optimized for efficiency, reliability, and real-time performance, making them indispensable in sectors such as healthcare and the Internet of Things (IoT). In medical devices, embedded operating systems (EOS) ensure precise control and functionality, facilitating timely responses that are critical for patient safety and device efficacy.
The market for integrated real-time software in healthcare is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated value of USD 5.66 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.97% from 2026 to 2032. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on integrated technologies in medical applications, where they support essential functions such as patient monitoring and data processing.
Recent advancements in integrated operating environments have enhanced their functionalities, particularly in IoT applications. For instance, Linux has become a favored choice among medical equipment manufacturers due to its robust security features and flexibility, allowing seamless integration with hospital IT networks and electronic health records (EHRs). A notable case study is GCE Healthcare's portable oxygen concentrator, which improved connectivity from 2G to Bluetooth and cloud integration, illustrating how integrated software can revolutionize patient care through real-time data collection and analysis.
Experts emphasize that the integration of an embedded operating system is vital for developing secure and efficient medical devices. As healthcare technology evolves, the adoption of sophisticated integrated solutions will continue to play a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
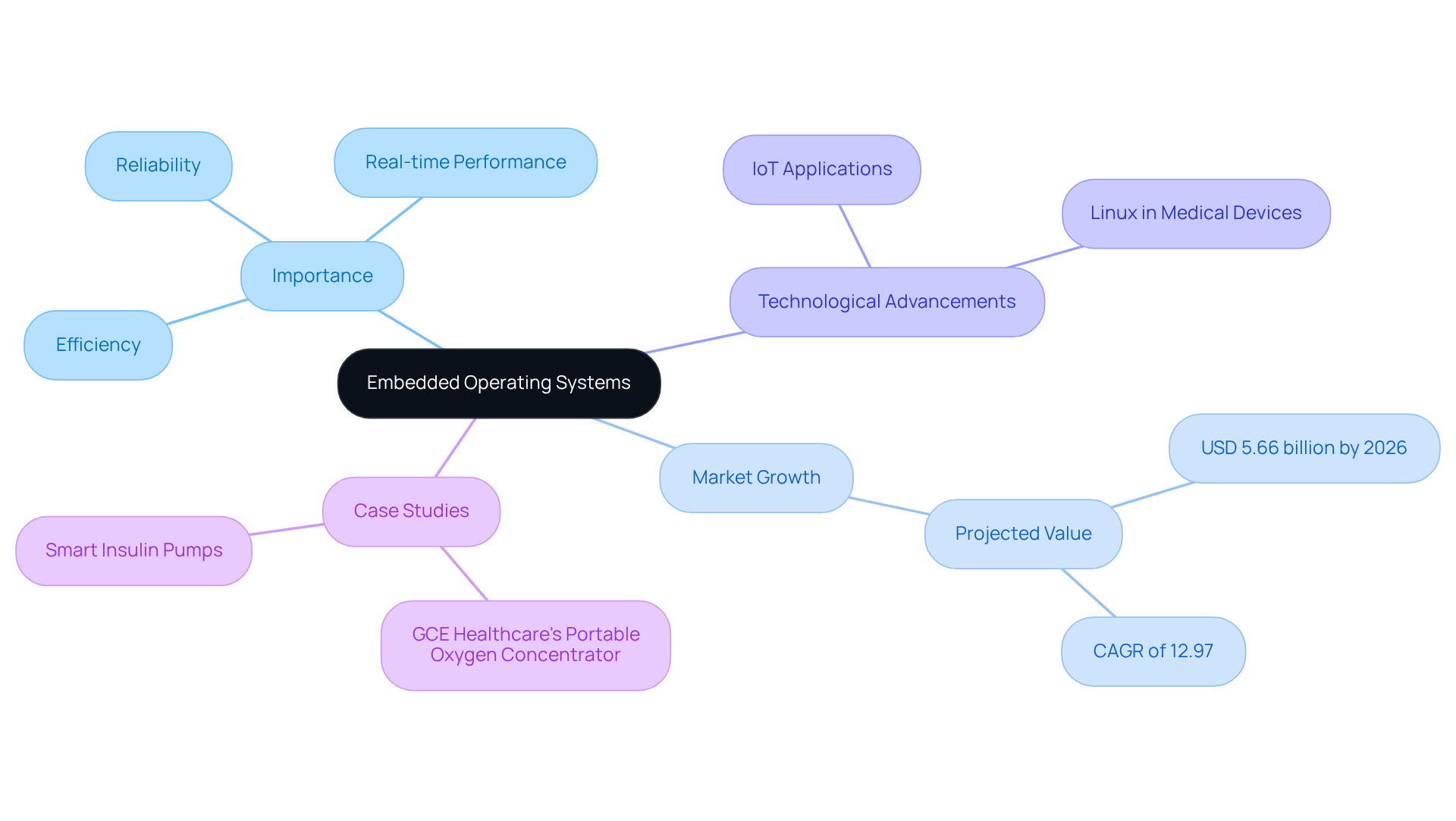
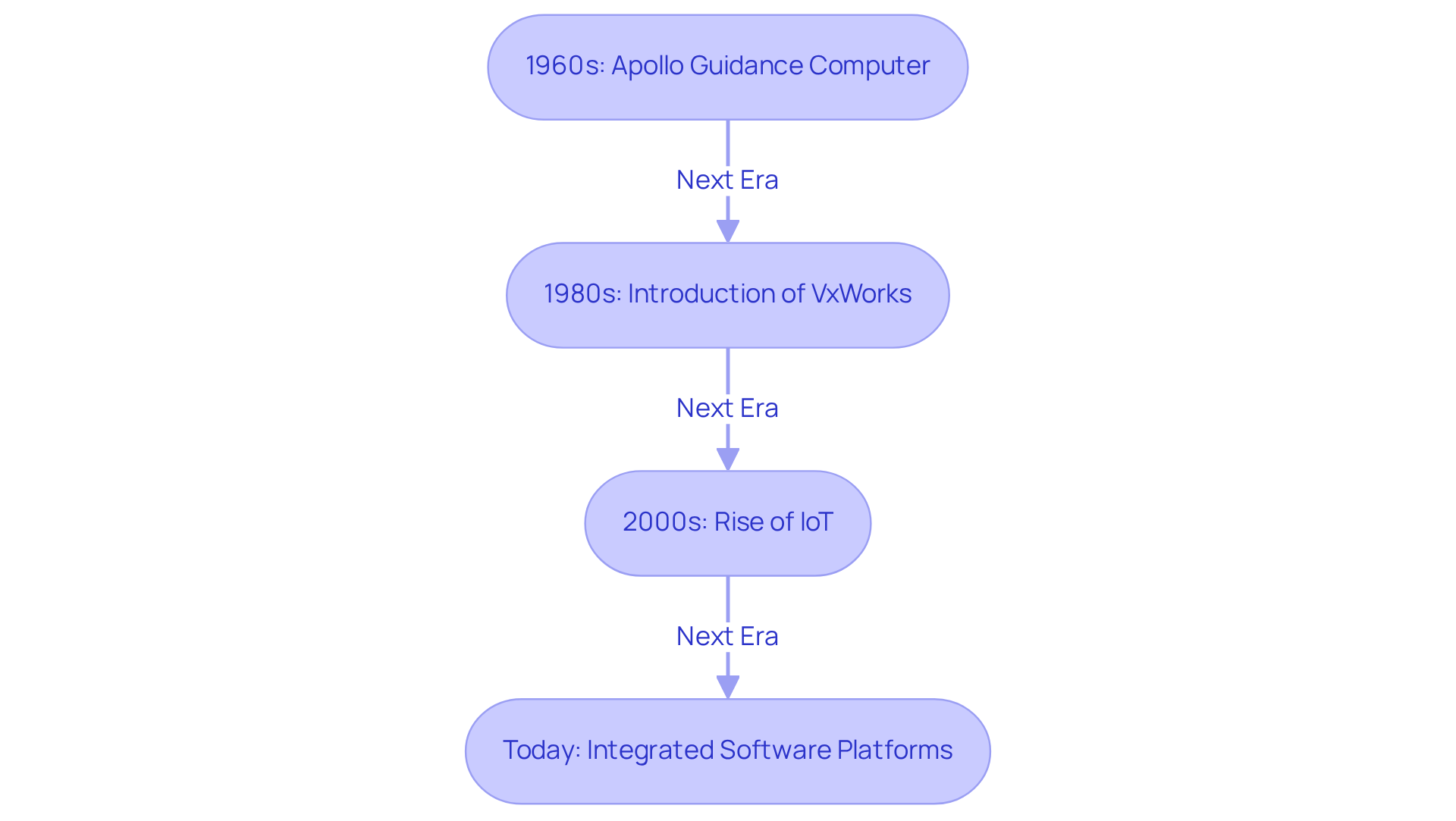
The development of integrated control platforms can be traced back to the late 1960s with the Apollo Guidance Computer, a pioneering integrated solution. The 1980s ushered in a transformative era with the introduction of embedded operating systems such as VxWorks, which enabled the creation of more sophisticated and responsive applications. This period represented a significant milestone, as RTOS began to integrate essential features like multitasking and networking capabilities, thereby enhancing their functionality across diverse hardware architectures.
As technology advanced, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the 2000s further propelled the evolution of embedded operating systems in integrated software. This led to the development of lightweight, efficient structures designed to function effectively in resource-constrained environments. Today, integrated software platforms are vital across a broad spectrum of applications, ranging from smart home devices to advanced medical equipment, underscoring their critical role in modern technology. The integrated processor market is projected to reach $44 billion by 2030, reflecting the growing demand for these technologies in various sectors, particularly in healthcare, where reliability and responsiveness are paramount.
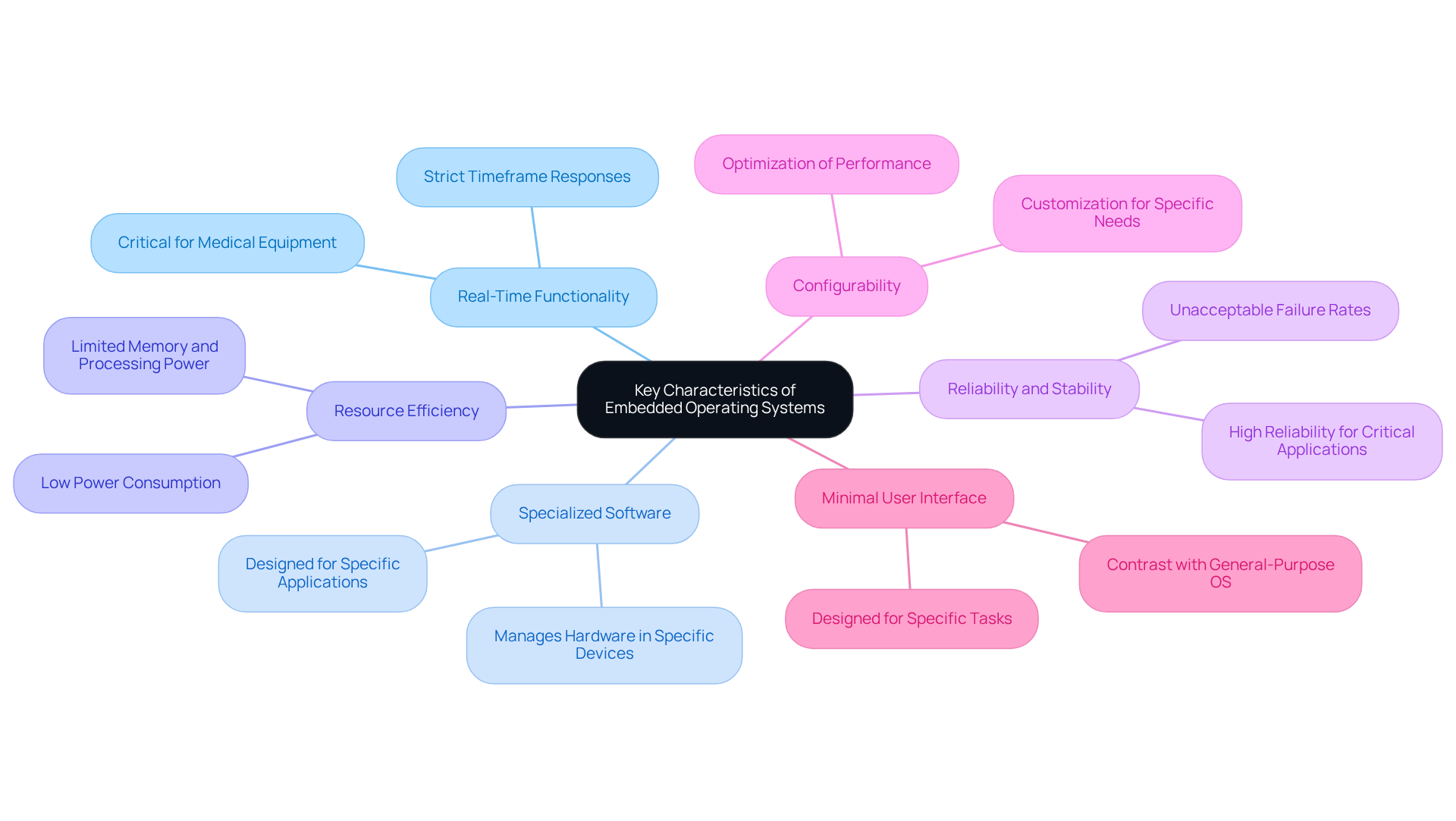
Key characteristics of embedded operating systems include:
Embedded operating systems often function in real-time, which means they can process data and respond to inputs within a strict timeframe. This capability is crucial for applications such as medical equipment, where delays can have serious consequences.
An embedded operating system is a specialized software designed to manage hardware in specific devices.
Resource Efficiency: Embedded operating systems are designed to function with limited resources, including memory and processing power. This makes them particularly suitable for devices that require low power consumption.
An embedded operating system is designed for specific applications. Reliability and stability are crucial for the software used in embedded operating systems, which must be highly reliable since these systems are frequently employed in critical applications where failure is unacceptable.
The device operates using an embedded operating system. Configurability: Many systems with an embedded operating system allow for customization to meet the specific needs of applications. This flexibility enables developers to optimize performance and functionality according to their requirements.
An embedded operating system is designed for specific tasks and is often used in devices like smartphones and appliances. Minimal User Interface: Unlike general-purpose operating systems, an embedded operating system typically features a minimal user interface, as it is designed for specific tasks rather than general use.
These characteristics ensure that embedded software can effectively meet the specific demands of the devices they control, particularly in fields such as healthcare and the Internet of Things (IoT), where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Real-world examples of embedded operating systems are common in various industries, especially in innovative medical device design projects by Voler Systems.
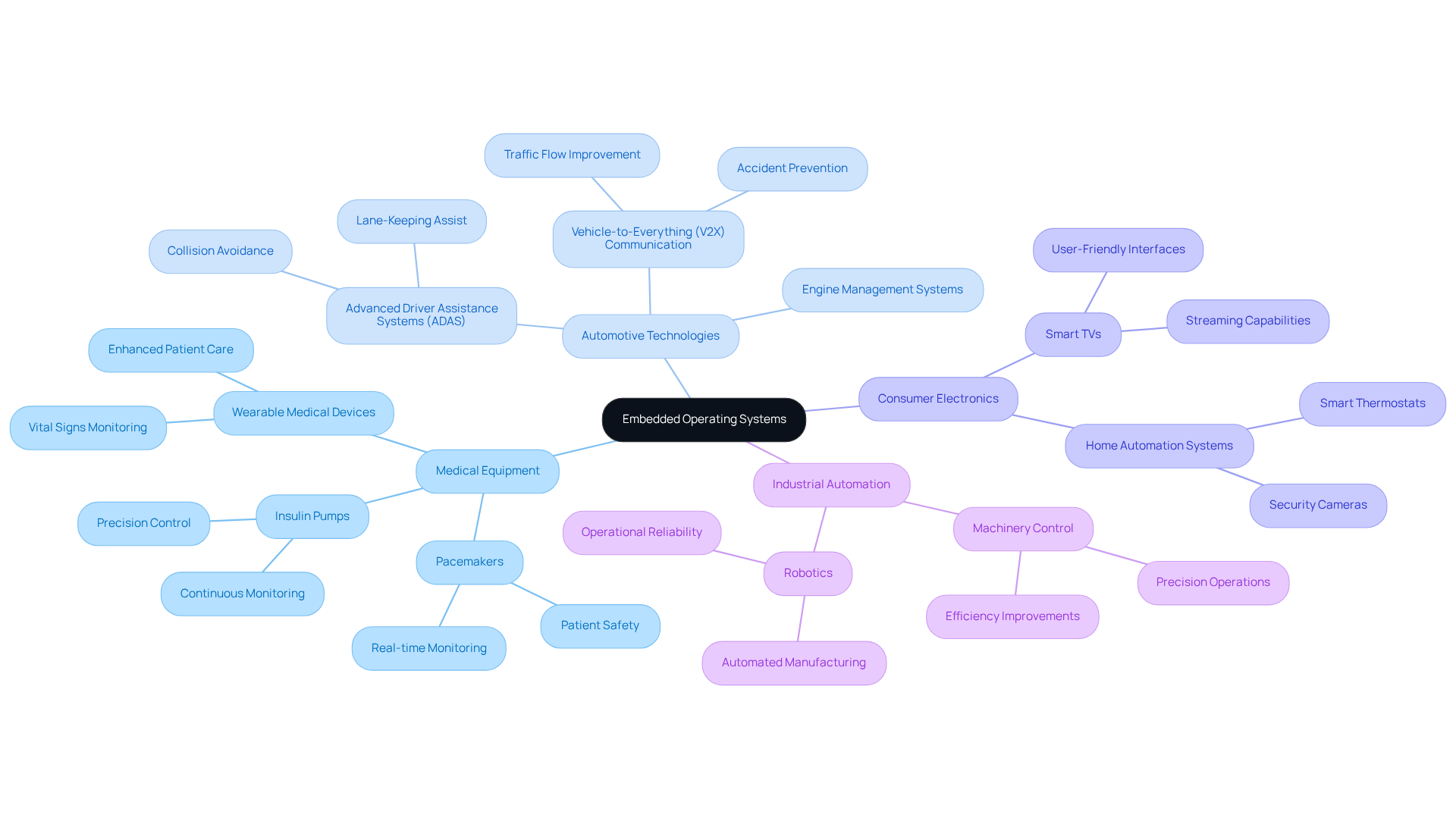
Medical equipment like pacemakers and insulin pumps rely on embedded operating systems, which are crucial for managing essential functions and ensuring patient safety through real-time monitoring and control. For example, Voler Systems has developed wearable medical devices that continuously monitor vital signs, demonstrating their expertise in creating solutions that enhance patient care. Case studies and testimonials underscore the positive impact of these innovations on patient outcomes.
Automotive Technologies: Modern vehicles utilize an embedded operating system for functions like engine management, navigation, and safety features, including anti-lock braking systems (ABS). These systems enhance both performance and security. Optimizing these frameworks is vital for the automotive sector, which is projected to experience significant growth.
Consumer Electronics: Devices such as smart TVs and home automation systems depend on embedded operating systems to deliver seamless user experiences and efficient operation. These frameworks enable customized features, thereby improving user satisfaction and engagement.
Industrial Automation: The embedded operating system plays a key role in managing machinery and robotics within manufacturing, ensuring precision and efficiency in production processes. The integration of operating systems in industrial applications leads to enhanced operational reliability and productivity.
These examples illustrate the versatility and significance of embedded operating systems in enhancing the functionality and reliability of devices across various sectors, especially in areas where Voler Systems operates, such as innovative ECG solutions and electronic motion detection.
Embedded operating systems serve as specialized software frameworks that manage hardware and software resources within dedicated devices. They play a crucial role in various sectors, including healthcare and the Internet of Things (IoT). Their distinct characteristics - such as real-time processing, resource efficiency, and reliability - set them apart from general-purpose operating systems, making them indispensable for applications where precision and timely responses are paramount.
This article has provided key insights into the evolution, significance, and practical applications of embedded operating systems. Tracing their origins back to the late 1960s, we have observed remarkable growth and adaptability, particularly in light of advancements driven by the IoT. The discussion has underscored their vital role in medical devices, automotive technologies, consumer electronics, and industrial automation, highlighting their substantial impact on enhancing device functionality and user experience.
As technology continues to advance, the importance of embedded operating systems is poised to increase further. Their capacity to deliver secure, efficient, and reliable solutions in critical applications emphasizes the necessity for ongoing innovation in this domain. Industries must recognize and harness the potential of embedded systems to enhance outcomes and operational efficiency, paving the way for a future where technology seamlessly integrates into everyday life.
What are embedded operating systems (EOS)?
Embedded operating systems are specialized software frameworks designed to manage hardware and software resources in dedicated devices that perform specific tasks, optimized for efficiency, reliability, and real-time performance.
Why are embedded operating systems important in healthcare?
In healthcare, embedded operating systems ensure precise control and functionality in medical devices, facilitating timely responses critical for patient safety and device efficacy.
What is the projected market growth for integrated real-time software in healthcare?
The market for integrated real-time software in healthcare is projected to grow to an estimated value of USD 5.66 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.97% from 2026 to 2032.
What role do embedded operating systems play in the Internet of Things (IoT)?
Embedded operating systems enhance functionalities in IoT applications, allowing for improved connectivity and data processing, which is essential for smart devices.
What operating system is favored by medical equipment manufacturers and why?
Linux is favored by medical equipment manufacturers due to its robust security features and flexibility, enabling seamless integration with hospital IT networks and electronic health records (EHRs).
Can you provide an example of how integrated software has improved patient care?
An example is GCE Healthcare's portable oxygen concentrator, which enhanced connectivity from 2G to Bluetooth and cloud integration, showcasing how integrated software can revolutionize patient care through real-time data collection and analysis.
What do experts say about the integration of embedded operating systems in medical devices?
Experts emphasize that integrating an embedded operating system is vital for developing secure and efficient medical devices, which will continue to enhance patient outcomes and operational efficiency as healthcare technology evolves.
