Potential FPGA Security Concerns and Solutions to Address Them
Field-programmable gate arrays, also known as FPGAs, are unique integrated circuits. They...

Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are transforming the medical device design landscape by providing exceptional flexibility and efficiency in a sector that requires rapid innovation and adherence to strict regulations. This article explores best practices for FPGA hardware design, emphasizing how engineers can utilize these powerful tools to improve performance, streamline development, and ensure safety in healthcare applications.
As the use of FPGAs increases, a critical question arises: how can designers effectively navigate the complexities of FPGA development to deliver reliable and advanced medical solutions?
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are versatile integrated circuits that can be configured post-production, offering substantial advantages in the healthcare device sector. Their inherent flexibility supports rapid prototyping and iterative design, which are essential in an industry marked by swift technological advancements and stringent regulatory requirements. Comprising an array of programmable logic blocks and interconnects, FPGA hardware design enables designers to create custom hardware solutions tailored to specific healthcare applications.
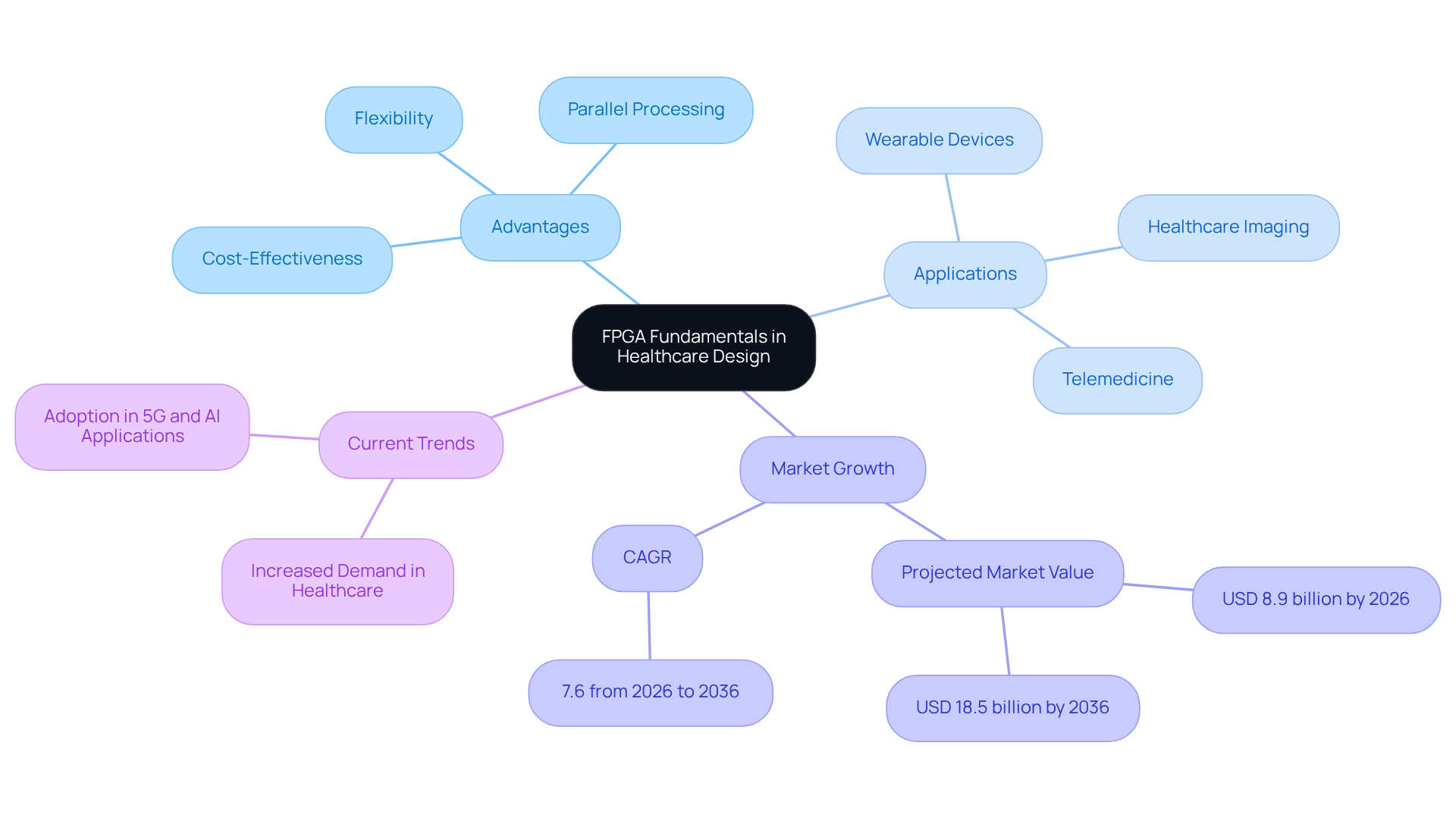
The ability of FPGAs to perform parallel processing makes them particularly efficient for high-speed data management tasks, such as real-time monitoring and diagnostics in medical equipment. For instance, wearable devices developed by Voler Systems leverage compact programmable logic designs to enhance wireless connectivity and optimize battery life, thereby facilitating continuous patient monitoring and prompt data transmission for telemedicine applications. By 2026, the global FPGA market is projected to reach USD 8.9 billion, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6%, driven by the increasing demand for high-performance computing and real-time data processing in healthcare.
Current trends indicate a rising dependence on FPGAs for advanced healthcare imaging systems, where they enable real-time image processing, thereby enhancing diagnostic clarity and speed. Additionally, the reprogrammable nature of FPGAs allows for rapid updates and adjustments to evolving healthcare standards, ensuring compliance and durability of equipment. By utilizing FPGA hardware design, engineers at Voler Systems can significantly reduce development time and enhance performance of equipment across various healthcare technologies, including heart pumps and liquid biopsy platforms. Furthermore, FPGAs present a cost-effective alternative to ASICs for low to medium volume applications, providing a compelling case for their adoption in healthcare equipment development.
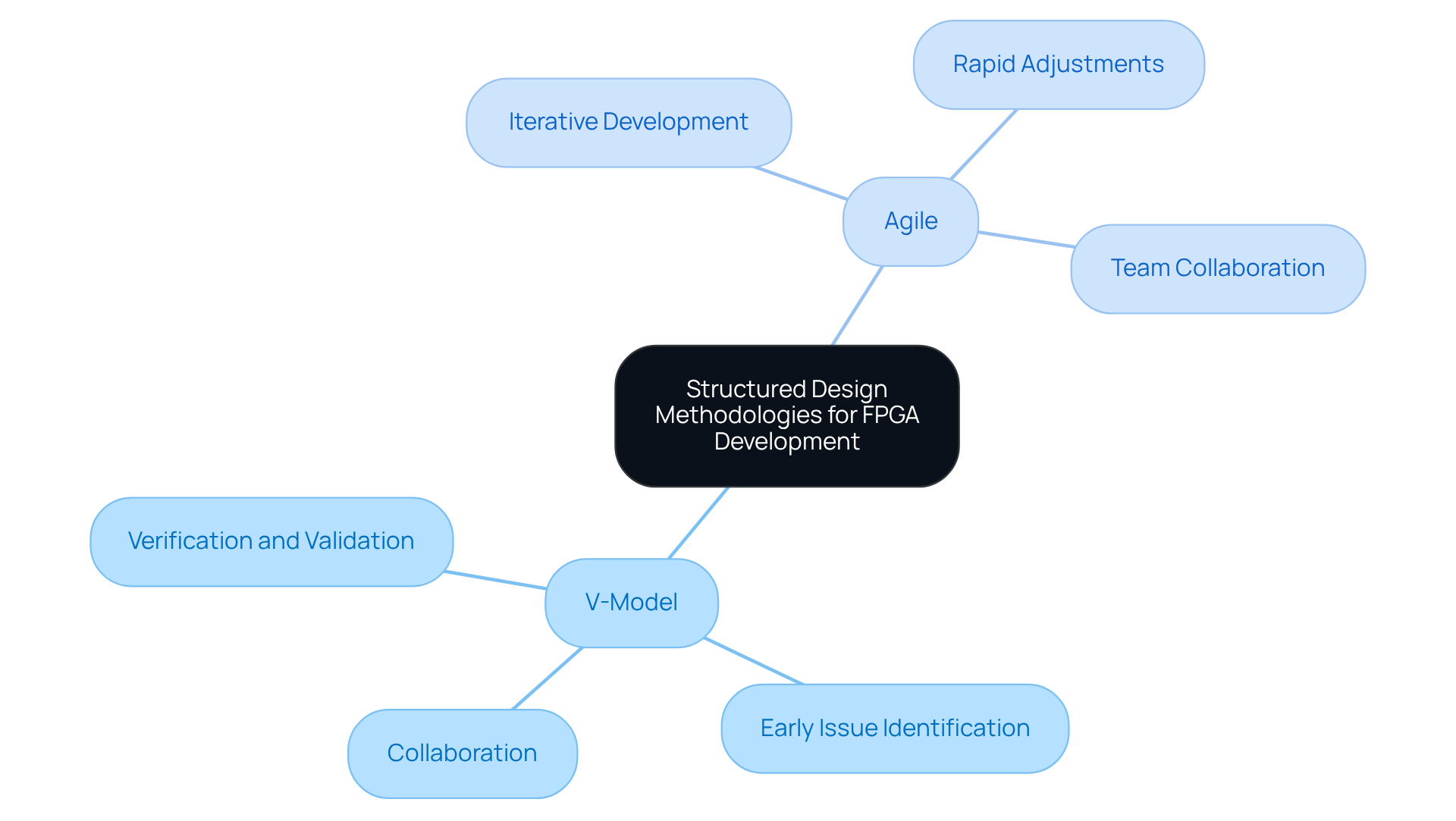
Applying organized development methodologies, such as the V-Model and Agile techniques, can significantly enhance the FPGA creation process for healthcare instruments. The V-Model emphasizes rigorous verification and validation at each design stage, ensuring that potential issues are identified early in the process. In contrast, Agile methodologies promote iterative development, allowing teams to make rapid adjustments based on testing feedback. Both methodologies encourage collaboration among cross-functional teams, which is crucial in device development, where insights from regulatory, clinical, and engineering experts are essential. By adopting these methodologies, teams can improve communication, streamline development timelines, and elevate the overall quality of the final product. Furthermore, leveraging the flexibility and cost efficiencies of programmable logic devices, Voler Systems provides documentation compliance assistance to effectively navigate regulatory challenges.
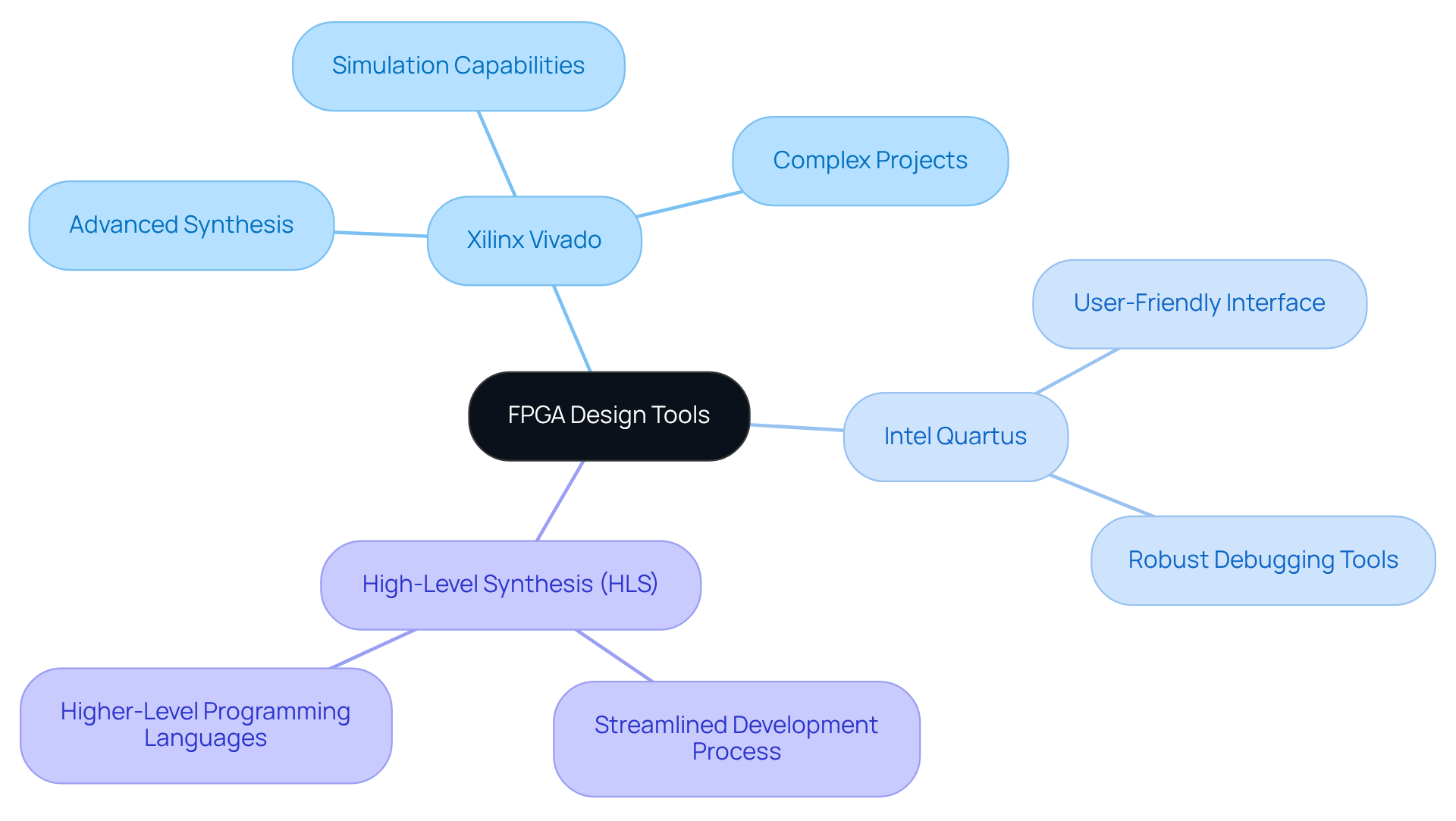
Selecting the appropriate tools for circuit implementation is essential for optimizing performance and efficiency, particularly in the demanding field of medical applications. Among the leading FPGA development software for FPGA hardware design are:
Each offering distinct advantages tailored to various project requirements. Xilinx Vivado is recognized for its advanced synthesis and simulation capabilities, which makes it particularly suitable for FPGA hardware design in complex projects. In contrast, Intel Quartus is noted for its user-friendly interface and robust debugging tools, which facilitate a more seamless user experience.
Furthermore, the integration of high-level synthesis (HLS) tools in FPGA hardware design allows engineers to utilize higher-level programming languages, thereby streamlining the development process compared to traditional hardware description languages (HDLs). To ensure timely and cost-effective delivery in electronic product development, engineers must effectively plan and execute projects, evaluate their likelihood of success, and identify when intervention is necessary to keep projects on track.
By thoroughly assessing project needs and selecting the most appropriate tools, engineers can significantly enhance productivity and achieve effective implementations. This is particularly relevant within the framework of Voler Systems' AI-driven engineering solutions, which simplify hardware development and adjustments for healthcare equipment manufacturing.
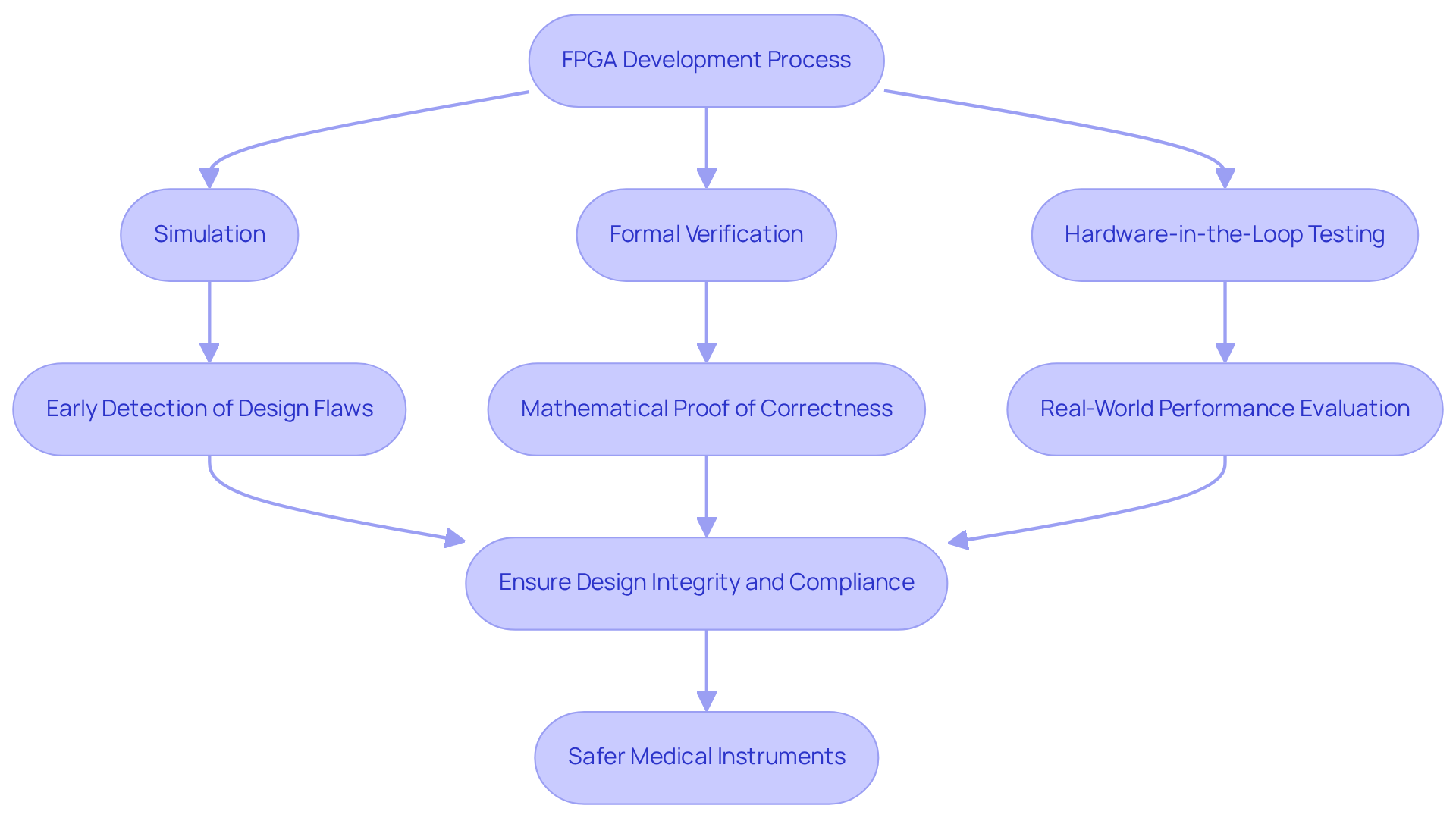
Incorporating testing and verification throughout the FPGA development process is essential for ensuring that medical instruments meet stringent functional and safety standards. Identifying common errors in manufacturing assessments, such as inadequate test coverage and the failure to replicate real-world conditions, is a critical step in this process. This recognition aids in ensuring quality and efficiency in the development of electronic devices.
Utilizing a combination of simulation, formal verification, and hardware-in-the-loop testing allows for comprehensive validation of concepts. Simulation enables the early detection of design flaws, facilitating timely corrections before the development of physical prototypes. Formal verification, which offers mathematical proof of correctness, is particularly vital in regulated sectors like healthcare, where compliance is imperative. Additionally, hardware-in-the-loop testing permits engineers to evaluate the FPGA's performance under real-world conditions, confirming its functionality across various scenarios.
By prioritizing these methodologies, engineers can significantly mitigate the risk of failures and enhance the reliability of their healthcare instruments, ultimately ensuring improved patient safety and satisfaction. Furthermore, documentation compliance support is crucial for startups in the medical device industry, assisting them in effectively navigating regulatory challenges.
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) represent a pivotal technology in medical device hardware design, providing unmatched flexibility and efficiency. Their capacity for post-production adaptation not only shortens development timelines but also ensures that healthcare devices can align with evolving standards and patient requirements. By leveraging the distinctive capabilities of FPGAs, medical device manufacturers can develop innovative solutions that improve patient monitoring, diagnostics, and overall healthcare delivery.
Key practices such as structured design methodologies, tool selection, and rigorous testing are essential for successful FPGA development. The V-Model and Agile methodologies promote collaboration and adaptability, while selecting appropriate development tools like Xilinx Vivado and Intel Quartus can significantly enhance the design process. Furthermore, prioritizing testing and verification is crucial for maintaining the integrity of medical devices, ensuring compliance with stringent industry regulations.
As the demand for high-performance computing in healthcare continues to escalate, adopting these best practices is vital for engineers and developers striving to advance medical technology. By integrating advanced FPGA design techniques and committing to quality and innovation, the potential for improved patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare solutions is substantial. The future of medical devices rests with those who are prepared to harness the power of FPGAs, making it essential to remain informed and proactive in implementing these best practices.
What are FPGAs and why are they important in hardware design?
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are versatile integrated circuits that can be configured after production. They are important in hardware design, particularly in the healthcare sector, due to their flexibility, which supports rapid prototyping and iterative design.
How do FPGAs benefit the healthcare device sector?
FPGAs offer significant advantages in healthcare by enabling high-speed data management, real-time monitoring, and diagnostics. Their ability to perform parallel processing enhances the performance of medical equipment, such as wearable devices for continuous patient monitoring.
What is the projected growth of the FPGA market?
The global FPGA market is projected to reach USD 8.9 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6%, driven by the demand for high-performance computing and real-time data processing in healthcare.
What trends are currently influencing the use of FPGAs in healthcare?
Current trends indicate an increasing dependence on FPGAs for advanced healthcare imaging systems, where they facilitate real-time image processing, improving diagnostic clarity and speed.
How do FPGAs ensure compliance with evolving healthcare standards?
The reprogrammable nature of FPGAs allows for rapid updates and adjustments to meet evolving healthcare standards, ensuring the compliance and durability of medical equipment.
What advantages do FPGAs provide over ASICs in healthcare applications?
FPGAs present a cost-effective alternative to Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) for low to medium volume applications, making them an attractive option for healthcare equipment development.
How does Voler Systems utilize FPGA hardware design?
Engineers at Voler Systems use FPGA hardware design to significantly reduce development time and enhance the performance of various healthcare technologies, including heart pumps and liquid biopsy platforms.
