How to Avoid Big Errors Using Accelerometers | Voler Systems
Accelerometers can be used to measure not only acceleration but also vibration....
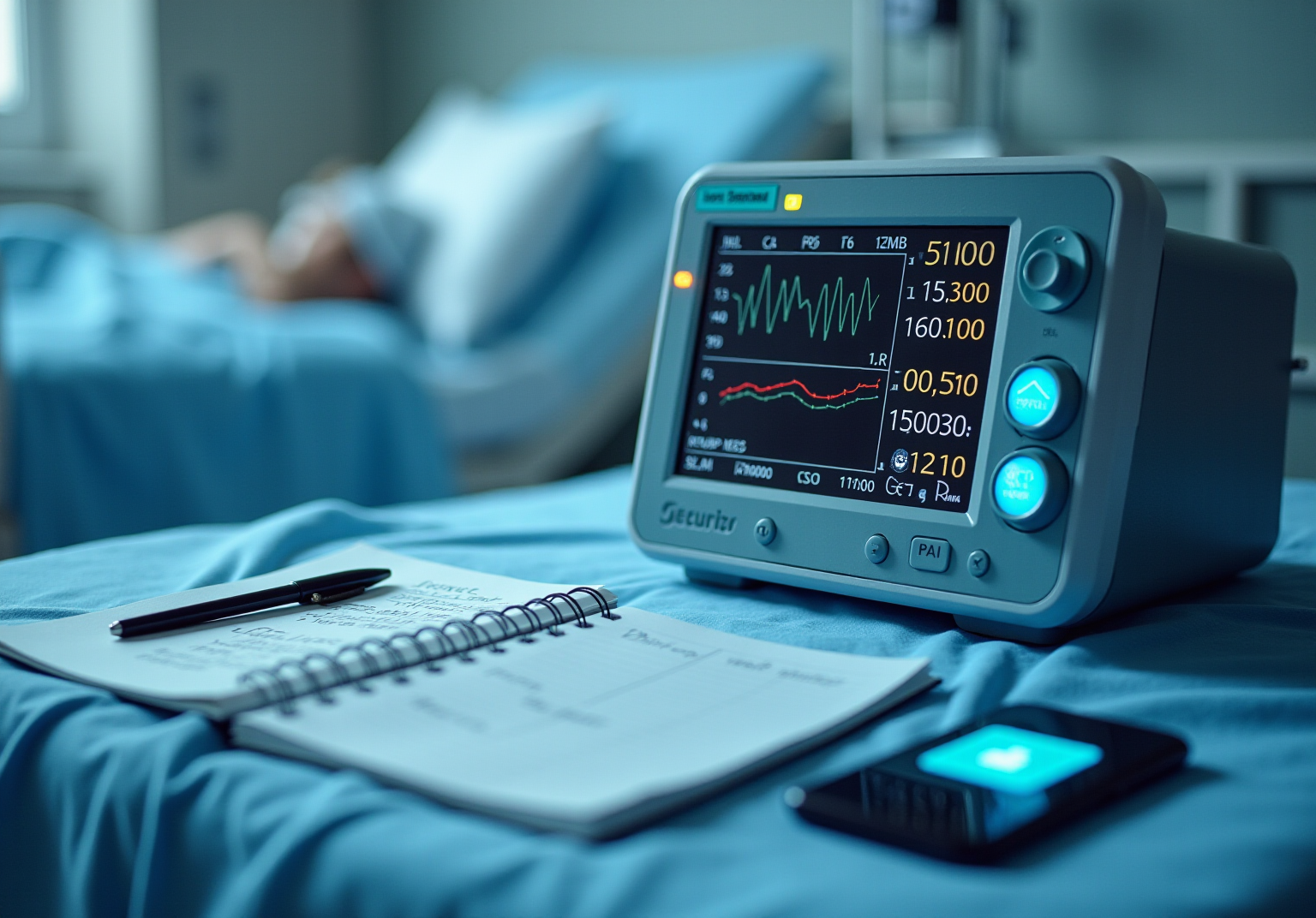

In an era marked by the increasing interconnectivity of medical devices, the significance of embedded system cybersecurity is paramount. As healthcare technology advances, so too do the threats aimed at sensitive patient data and device functionality. This reality underscores the necessity for manufacturers to implement robust security measures.
This article examines best practices for bolstering cybersecurity in medical devices, highlighting essential strategies such as:
How can manufacturers ensure that their devices not only meet stringent regulatory standards but also remain resilient against the constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats?
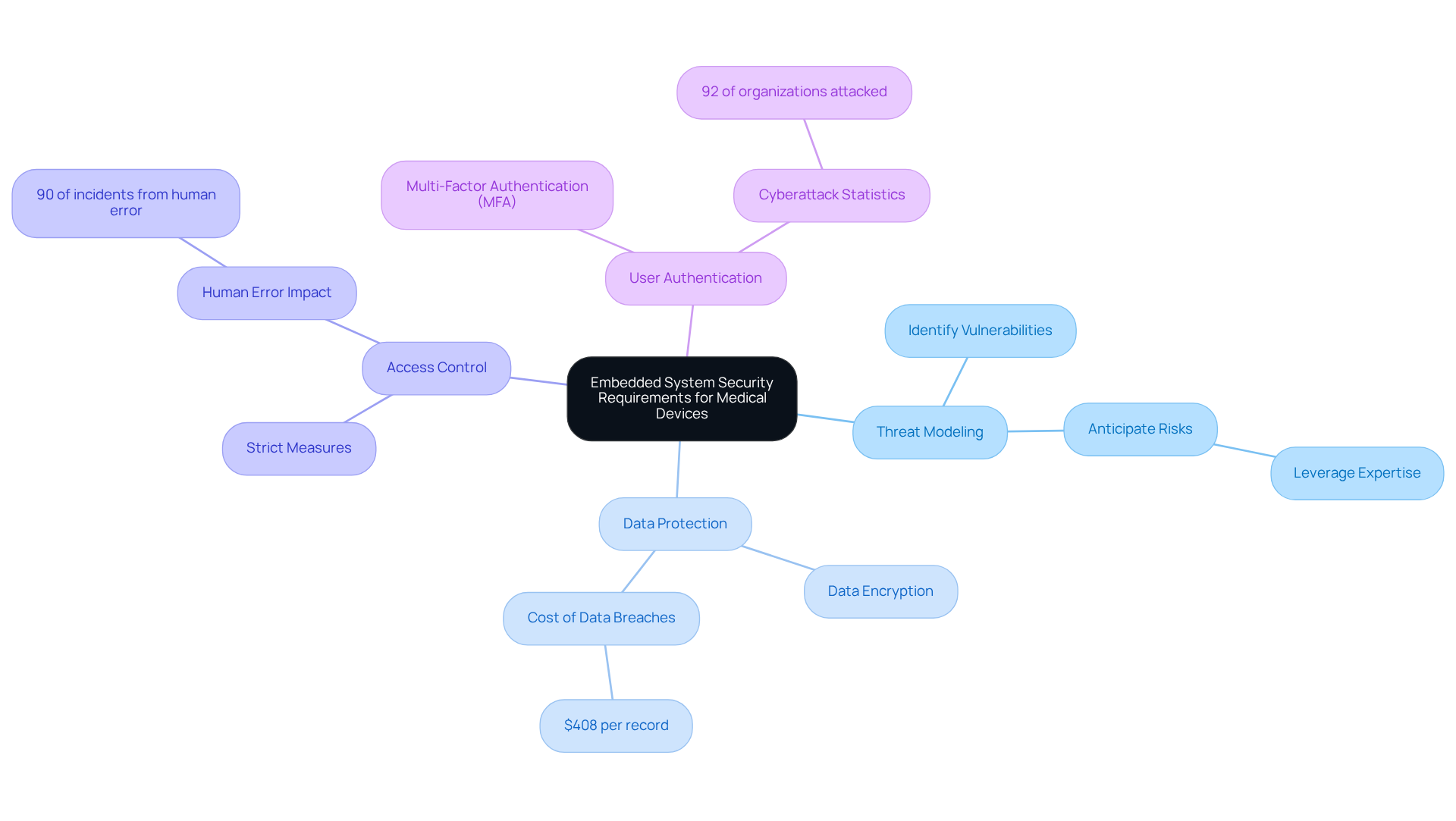
To effectively ensure embedded system cyber security in medical equipment, it is essential to understand the specific security requirements that govern their design and operation. This includes recognizing the unique challenges posed by connectivity, data privacy, and regulatory compliance. Key considerations are as follows:
By addressing these requirements early in the design phase, manufacturers can create more secure products that not only meet user needs but also comply with stringent regulatory standards. The incorporation of threat modeling best practices into the design process is crucial for developing robust healthcare instruments capable of withstanding evolving cyber threats, reflecting the importance of embedded system cyber security in Voler Systems' approach to innovative health technology development.
Integrating security-by-design principles is essential for developing resilient medical devices. This proactive approach ensures that protective measures are embedded throughout the entire development lifecycle. Key practices include:
By embedding protection into the design process, manufacturers can create products that are not only functional but also resilient against evolving cyber threats, ultimately enhancing patient safety and confidence in healthcare technology through embedded system cyber security.
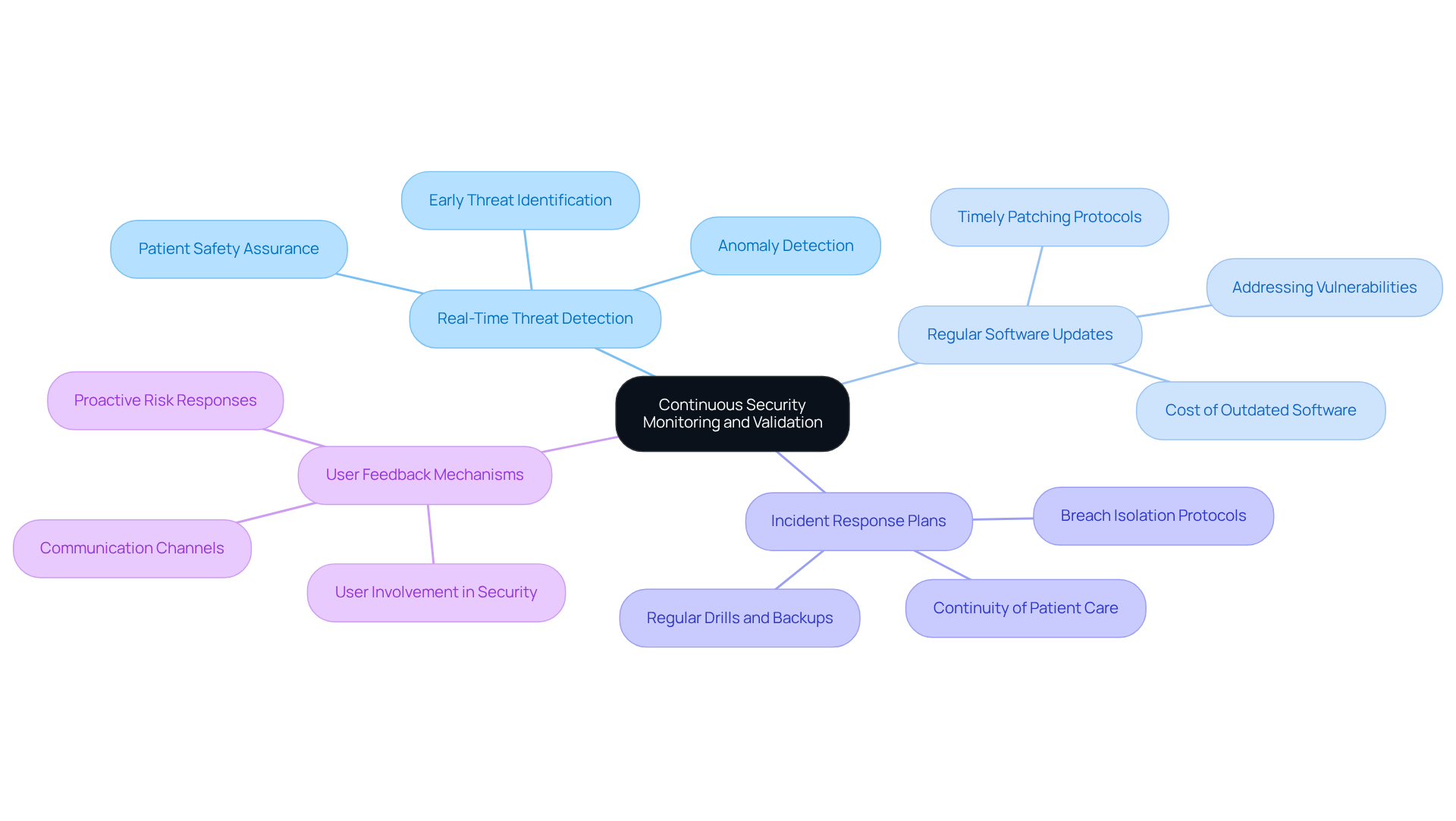
To ensure the ongoing protection of embedded systems in medical equipment, it is essential to focus on embedded system cyber security through continuous monitoring and validation. This involves:
Real-Time Threat Detection: Implement systems that provide real-time monitoring of device activity to detect anomalies and potential security breaches. Such systems, utilizing embedded system cyber security, are vital as they can identify threats before they escalate, significantly reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring patient safety.
Regular Software Updates: Establish a protocol for regular software updates and patches to address newly discovered vulnerabilities. By 2026, healthcare organizations should prioritize timely updates, as outdated software remains a primary target for cybercriminals. The average cost of a data breach in healthcare has reached $10 million, highlighting the financial necessity of maintaining updated systems.
Incident Response Plans: Develop and maintain incident response plans to swiftly address any breaches that may occur. These plans should include protocols for isolating compromised equipment and ensuring that patient care continues safely during an incident.
User Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for users to communicate concerns or irregularities, enabling proactive responses to potential risks. Involving users in the security process can enhance the overall security posture of healthcare equipment, as they often serve as the initial line of defense against emerging threats.
By maintaining constant observation and verification, manufacturers can quickly adapt to new risks and ensure the ongoing safety and efficacy of their healthcare products, particularly by addressing embedded system cyber security.
Adherence to regulatory standards is essential in the development of medical equipment, particularly concerning cybersecurity. Key steps include:
Familiarization with Regulations: Regularly update your knowledge of relevant regulations, including the FDA's cybersecurity guidelines, to ensure compliance throughout the device lifecycle. The FDA emphasizes that manufacturers must provide reasonable assurance of cybersecurity for their products, marking a shift from previous priorities focused solely on safety and effectiveness.
Documentation Practices: Maintain comprehensive documentation of protective measures, risk assessments, and validation processes. This documentation is vital for demonstrating compliance during audits and must include a cybersecurity management plan and a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) to effectively identify vulnerabilities. The FDA mandates that these documents be part of the eSTAR submission process to prevent refusal to accept decisions.
Engagement with Regulatory Bodies: Establish proactive communication with regulatory bodies to clarify requirements and seek guidance on compliance strategies. This engagement aids in navigating the complexities of regulatory expectations and ensures that all necessary documentation is in place.
Adoption of Industry Standards: Adhere to established industry standards such as IEC 62304 and ISO 14971, which provide frameworks for managing safety and security risks in medical equipment. The ANSI AAMI SW96 standard, recognized for its formal requirements, encourages manufacturers to integrate cybersecurity principles into their design controls and risk assessments.
By prioritizing compliance with these regulatory standards and best practices, manufacturers can enhance the credibility of their devices and facilitate smoother market entry.
Ensuring the cyber security of embedded systems in medical devices is not merely a technical necessity; it is a fundamental responsibility that manufacturers must embrace. By understanding specific security requirements, implementing security-by-design principles, maintaining continuous security monitoring, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, manufacturers can significantly enhance the resilience of their products against evolving cyber threats.
The article highlights several key practices essential for achieving robust embedded system cyber security. These include:
Additionally, integrating security throughout the development lifecycle and maintaining vigilant monitoring are critical to safeguarding sensitive patient information and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
As the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, it is imperative for manufacturers to adopt these best practices proactively. Emphasizing a culture of security within the development process not only protects patients but also fosters trust in healthcare technology. The commitment to embedded system cyber security must be unwavering, as it is integral to the integrity and safety of medical devices in today's interconnected healthcare environment.
What are the key security requirements for embedded systems in medical devices?
The key security requirements include threat modeling, data protection, access control, and user authentication.
Why is threat modeling important in the design of medical devices?
Threat modeling is crucial for identifying potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors specific to the device's functionality and connectivity, allowing manufacturers to anticipate and mitigate risks effectively.
How can data protection be ensured in medical devices?
Robust data encryption methods should be implemented to safeguard sensitive patient information, both at rest and in transit, to protect against data breaches.
What role does access control play in medical device security?
Establishing strict access control measures ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive system components, which helps prevent unauthorized access and reduces the risk of healthcare data breaches.
What is the significance of user authentication in medical devices?
Employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security for user access, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized entry, especially in light of the high incidence of cyberattacks in healthcare organizations.
How can manufacturers create more secure medical devices?
By addressing security requirements early in the design phase and incorporating threat modeling best practices, manufacturers can develop secure products that comply with regulatory standards and meet user needs.
